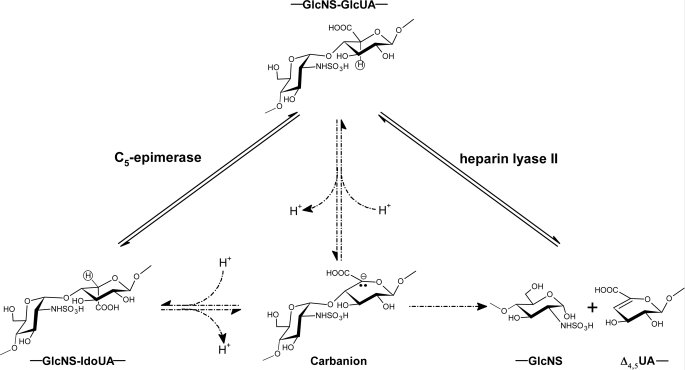
FIGURE 6.
Proposed catalytic mechanisms of C5-epi and heparin lyase II (34). Both C5-epi-catalyzed (left) and heparin lyase II-catalyzed (right) reactions go through the same carbanion intermediate by abstracting the C5 proton. This carbanion intermediate can be reprotonated (left) to produce epimerized product or proceed to an elimination reaction by breaking up the glycosidic bond (right). Left, the C5 proton is shown in a circle, which can be 3H-labeled.