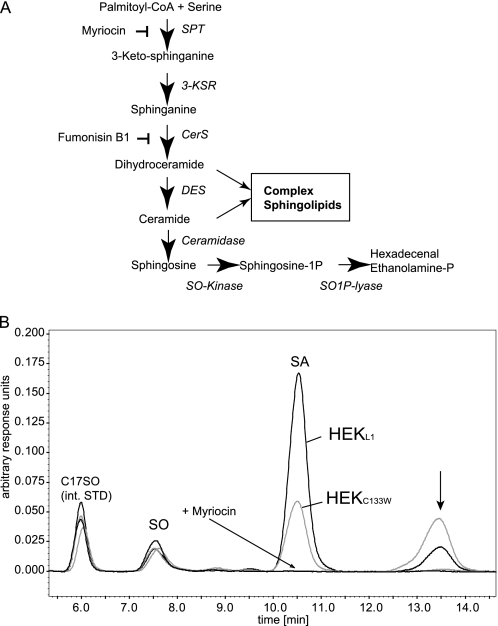
FIGURE 1.
A, de novo sphingolipid synthesis pathway. De novo ceramide synthesis involves several steps. SPT catalyzes the initial conjugation of palmitoyl-CoA with l-serine to form 3-keto-sphinganine, which is subsequently reduced to SA. SA is acetylated by ceramide synthase (CerS) and desaturated by ceramide desaturase (DES) to form ceramide. The degradation pathway starts with the deacetylation of ceramide by ceramidase. The formed SO is then phosphorylated by SO-kinase and finally degraded to hexadecenal and phosphoethanolamine by the action of the sphingosine-1-phospate lyase (SO1P lyase). B, HEK293 cells expressing the SPT-C133W mutant generate an unknown metabolite. HEK293 cells were transfected with either wild-type SPTLC1 or the SPTLC1-C133W mutant. De novo synthesis was blocked with FB1 for 24 h. This causes an accumulation of sphinganine but also of other potential SPT products. The accumulated sphingoid bases were extracted and analyzed by HPLC. We observed a significant accumulation of SA in HEKL1 cells (black). SA accumulation was lower in HEKC133W cells (gray), which reflects the reduced activity of the mutant. In parallel, we observed the appearance of a second, unknown peak (arrow). This peak appeared only in the presence of FB1 and was increased in cells expressing the C133W mutant. It was absent when SPT activity was blocked with myriocin. int. STD, internal standard.