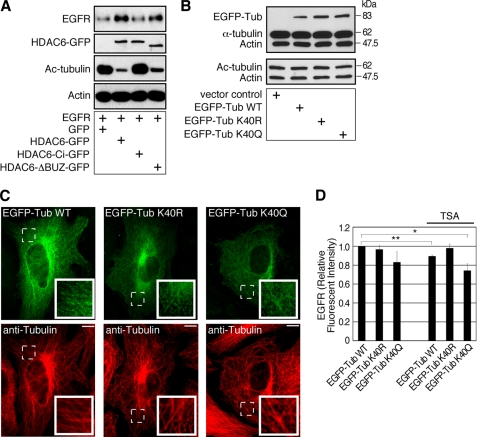
FIGURE 5.
Tubulin acetylation regulates EGFR in the cells. A, HDAC6 knock-out MEFs re-expressing control GFP, HDAC6-GFP, HDAC6-Ci-GFP, or HDAC6-ΔBUZ-GFP were engineered to express EGFR. Cell lysates were examined by immunoblotting using anti-EGFR, anti-GFP, anti-acetyl-tubulin, and anti-β-actin antibodies. The EGFR level was inversely correlated to tubulin acetylation. (GFP band in GFP control group was not shown.) B, 293T cells were transfected for 3 days with a control vector, EGFP-α-tubulin WT, EGFP-α-tubulin K40R, or EGFP-α-tubulin K40Q plasmid. Cell lysates were examined by immunoblotting using a mixture of anti-α-tubulin and anti-β-actin antibodies, or a mixture of anti-acetylated tubulin and anti-β-actin antibodies. C, MEFs were transfected with constructs as in B for 2.5 days, and the microtubules were visualized by immunofluorescence using an anti-tubulin antibody. The exogenous EGFP-tagged α-tubulin became a part of the microtubule network. Insets, enlarged areas marked by dotted lines. Bars, 10 μm. D, 293T cells were co-transfected with EGFR-pcDNA and EGFP-α-tubulin WT, EGFP-α-tubulin K40R, or EGFP-α-tubulin K40Q for 3 days. For the last 8 h of transfection, cells were treated with only cycloheximide or TSA and cycloheximide. Cells were immunostained for EGFR and examined by flow cytometry. **, p < 0.01 and *, p < 0.05 in two-tailed and paired Student's t test, n = 5. Error bars, S.E.