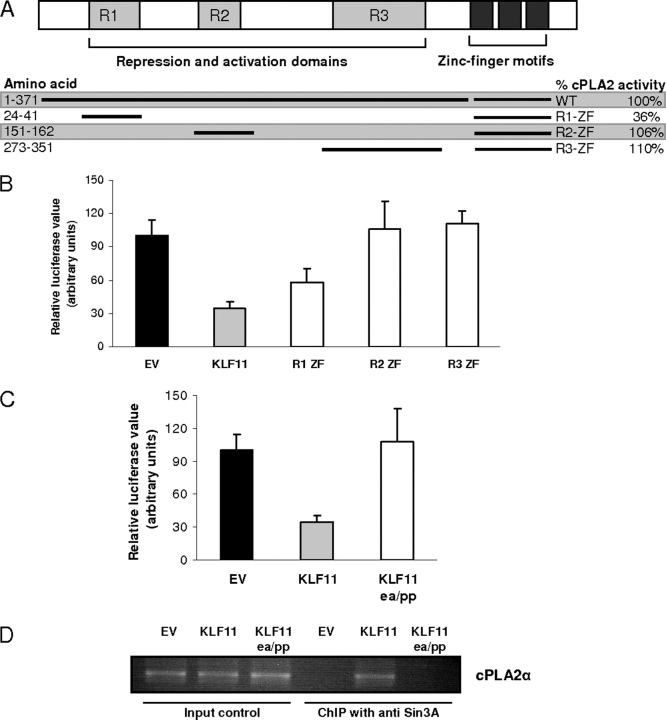
FIGURE 4.
R1 repressor domain of KLF11 is critical in the cPLA2α promoter repression via binding and function of the Sin3a-HDAC chromatin remodeling complex.A, the top panel shows the outline of repressor and DNA binding domains of the KLF11 protein. The lower panel is a summary as described in the legend to Fig. 3B. B, FLO cells were co-transfected with the cPLA2α promoter reporter construct along with either empty vector or full-length KLF11 or KLF11 deletions containing distinct regulatory domains. Compared with empty vector control, both full-length and R1-ZF KLF11 significantly repressed cPLA2α promoter activity (65.6 ± 12 and 42.4 ± 9.8%, p < 0.05) but R2-ZF and R3-ZF failed to repress the cPLA2α promoter activity. C, in FLO cells, compared with control, wild-type KLF11 repressed the cPLA2α promoter activity by 65.6 ± 12% (p < 0.05), the ΔE29P/ΔA30P-KLF11 (the mutant to disrupt Sin3a-HDAC binding) completely abolished cPLA2α repression by KLF11. D, ChIP assay using FLO cell lysates shows that the cis-regulatory cPLA2α promoter sequence is enriched in anti-Sin3a antibody (SC-994) immunoprecipitated samples from cells infected with adenovirus carrying wild-type KLF11 (fifth lane from the left) but absent in adenovirus carrying the ΔE29P/ΔA30P-KLF11 mutation (sixth lane from the left) demonstrating that the KLF11-mediated recruitment of Sin3a to the cPLA2α promoter can be abrogated by the ΔE29P/ΔA30P mutation in KLF11. The input controls are in the first three lanes on the left and similar results were noted in SEG-1 cells (data not shown). Together, the data support that the R1 domain of KLF11 is critical in repression of the cPLA2α promoter and this repression is Sin3a-HDAC-dependent.