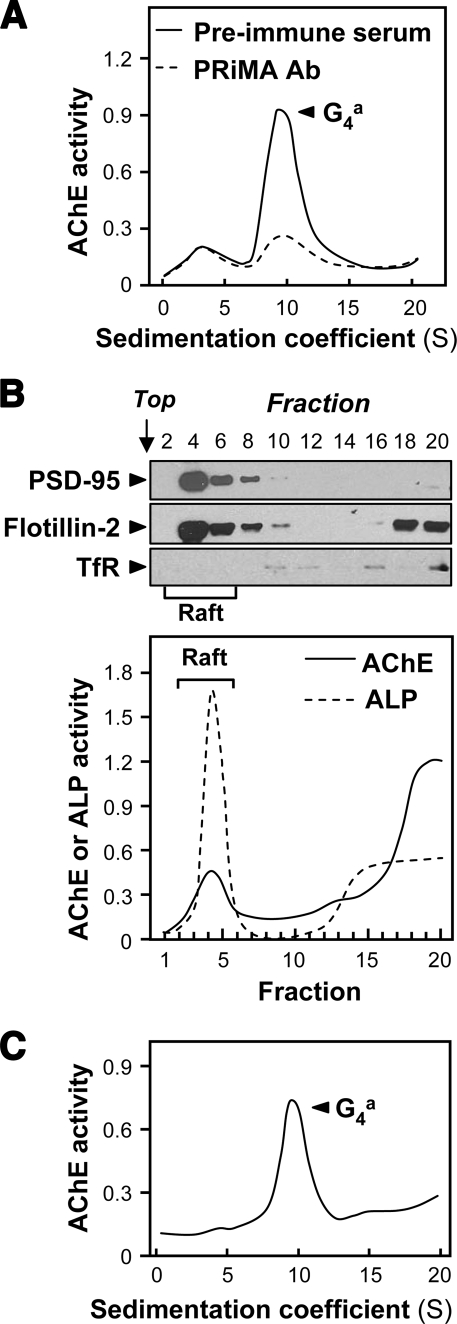
FIGURE 1.
Adult rat brain contains PRiMA-linked G4 AChE in membrane rafts. A, total membrane fraction was isolated from 400 mg of fresh tissue samples of adult rat cerebrum; AChE was solubilized with 0.5% Triton X-100 and analyzed by sedimentation in sucrose gradients containing 0.2% Brij-97. To verify the presence of PRiMA, an aliquot of the extract was incubated with anti-PRiMA antibody (Ab) (10 μg/ml). After the precipitation by protein G-agarose, the supernatant was subjected to sucrose density gradient analysis. Preimmune serum was used in the control. In the sedimentation profiles, AChE activity (arbitrary units) is plotted as a function of the sedimentation coefficients, determined with the internal standards β-galactosidase (16 S) and ALP (6.1 S). The major AChE component 9.1 S corresponds to amphiphilic tetramers (G4a). B, AChE activity from cerebrum membranes in detergent-resistant (raft; fractions 2–6) and detergent-soluble (non-raft) fractions was determined after flotation in discontinuous sucrose gradients with 0.5% cold Triton X-100. Aliquots of each even fraction were analyzed by 8% SDS-PAGE, and the expressions of PSD-95 (∼95 kDa), flotillin-2 (∼55 kDa), and transferrin receptor (∼70 kDa) are shown in Western blots as controls (upper panel). Enzymatic activities of AChE and ALP are expressed in arbitrary units (lower panel). ALP serves as control to identify raft-enriched fractions. TfR, transferrin receptor. C, sedimentation profile of AChE solubilized from the raft-enriched fractions of cerebrum from B was determined. The sedimentation was performed as in A. The profile shows a single molecular form at 9.1 S corresponding to amphiphilic tetramers. For all sedimentation analyses, one representative profile is shown, n = 3.