FIGURE 3.
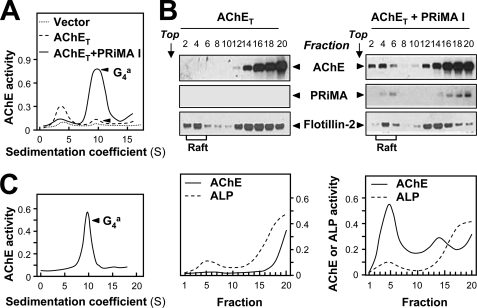
PRiMA directs amphiphilic G4 AChE to the membrane raft in transfected cells. A, NG108-15 cells were transfected with an empty control vector as a control and with a vector encoding AChET-HA without or with a vector encoding PRiMA I-HA. The sedimentation profiles of AChE from cell extracts showed that co-transfection with AChET and PRiMA I produced an amphiphilic tetramer at 9.1 S. Sedimentation was performed as in Fig. 1A. B, AChE activity in detergent-soluble (bottom) and detergent-resistant (Raft) fractions was revealed after flotation in discontinuous sucrose gradients in the presence of 0.02% Triton X-100 (low) in the cold. Enzymatic activities are expressed in arbitrary units (lower panel). Aliquots of even fractions were analyzed by 12% SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with an anti-HA antibody to detect AChE (∼68 kDa) and PRiMA (∼20 kDa), and with an antibody against flotillin-2 (∼55 kDa), which served as a membrane raft marker (upper panel). C, sedimentation profile of AChE, solubilized from the low density membrane raft fractions, from cells expressing AChET and PRiMA I (B). The sedimentation was performed as in A. The profile shows a single molecular form at 9.1 S, corresponding to amphiphilic tetramers. For all sedimentation analyses, one representative profile is shown, n = 3.