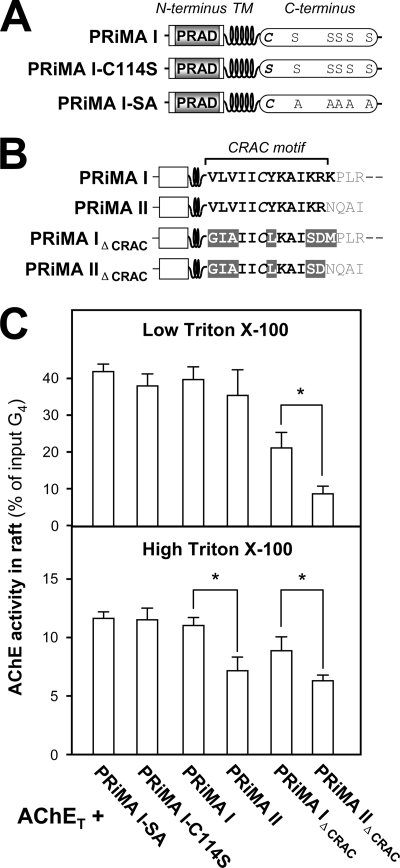
FIGURE 8.
Role of the C-terminal cytoplasmic domain of PRiMA in the association of PRiMA-linked AChE with membrane rafts. A, schematic representation for the difference among wild type PRiMA I, mutant in which the putative palmitoylation site was suppressed (PRiMA I-C114S) and mutant in which all potentially phosphorylated serines were replaced by alanines (PRiMA I-SA). B, schematic representation for the difference among wild type PRMA I, PRiMA II in which the C-terminal residues (NQAI) differ from those of PRiMA I, PRiMA IΔCRAC (VLVIICYKAIKRK→GIAIICLKAISDM) as in Fig. 5, and PRiMA IIΔCRAC (VLVIICYKAIKR→GIAIICLKAISD). C, proportions of AChE activity recovered in the raft fractions after flotation in discontinuous sucrose gradients, in the presence of low (0.02%) or high (0.2%) Triton X-100 in the cold. The raft-associated AChE activity was determined. The values, expressed as % of the total G4 AChE activity input in the discontinuous gradient, are means ± S.E. (n = 4). *, p < 0.05.