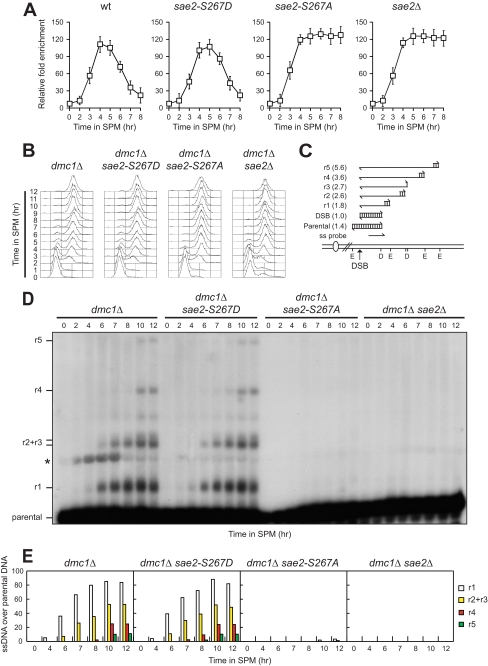
FIGURE 3.
Phosphorylation of Sae2 Ser-267 is essential for both Spo11 removal and DSB resection. A, Spo11-DNA association. Chromatin samples taken at different time points after meiosis induction were immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc antibody. Coimmunoprecipitated DNA was analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR using primer pairs located 162 bp (DSB) and 2319 bp (CON) distal to the DSB site of the YCR048W hotspot. Data were expressed as the -fold enrichment of DSB over CON signal after normalization to input signals for each primer set. The data presented are the mean of those obtained in three independent experiments. Error bars indicate ±S.D. B, synchronous meiotic cultures of cells with the indicated genotypes were analyzed at the indicated times for DNA content by FACS. C, scheme of the system used to detect DSB resection at the YCR048W hotspot. Genomic DNA was digested with both DraIII (D) and EcoRV (E), and DNA fragments were separated on alkaline agarose gel. Gel blots were hybridized with a single-stranded RNA probe, which reveals an uncut fragment of 1.4-kb (parental). DSB formation and subsequent 5′-to-3′ resection eliminate DraIII and EcoRV sites, thus producing larger DNA fragments (r1, r2, r3, r4, and r5) detected by the probe. D, genomic DNA prepared from samples taken at the indicated times during the experiment in B was analyzed for ssDNA formation as described in C. The asterisk points out an unspecific signal. E, densitometric analysis of the representative experiment shown in D. Values are expressed as arbitrary units. Three independent experiments were performed with very similar results.