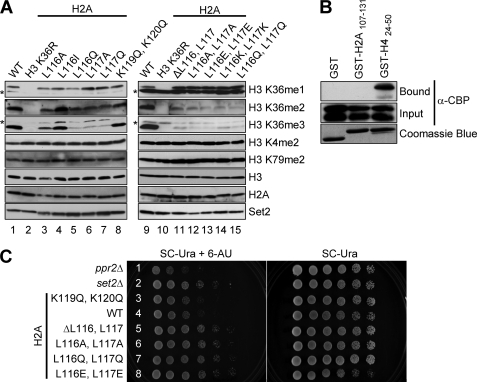
FIGURE 3.
Histone H2A Leu116 and Leu117 are needed for trans-histone H3 Lys36 di- and trimethylation in vivo and for appropriate 6-AU sensitivity. A, whole cell extracts prepared from cells expressing WT histones or the indicated histone mutants are immunoblotted with H3 Lys4, H3 Lys36, and H3 Lys79 methyl-specific antibodies. The asterisks denote nonspecific bands. Immunoblots for histone H3 and H2A serve as loading controls. The Set2 proteins levels are detected by probing with an α-Set2 antibody. B, C-terminal tail of histone H2A does not bind to recombinant Set2. In vitro binding assays are performed using GST, GST-H424–50, or GST-H2A107–131, incubated with CBP-Set2 extracts. Bound and input amounts of CBP-Set2 protein are detected by immunoblotting with an α-CBP antibody. The amount of GST, GST-H4, or GST-H2A fusion protein used in the assays is analyzed by Coomassie Blue staining. C, strains with H3 Lys36 methylation defects shown in A exhibit 6-AU resistance. Yeast cells expressing WT or the indicated histone H2A mutants are assayed for growth in the presence or absence of 6-AU (150 μg/ml). The ppr2Δ and set2Δ strains serve as controls for 6-AU sensitivity and resistance, respectively.