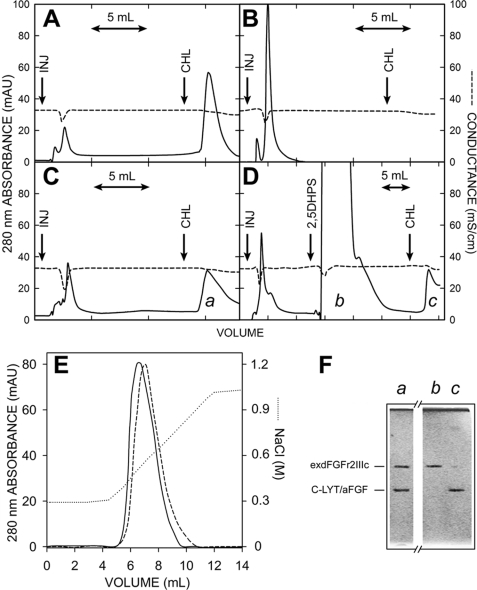
FIGURE 8.
Chromatography of C-LYT/aFGF·exdFGFR2IIIc complexes. The protein (∼3.2 nmol in each case) was injected in 250 μl of the chromatography buffer at the arrows labeled INJ. The buffer contained 150 mm choline from the mark (arrow labeled CHL) to the end of the chromatogram. A, C-LYT/aFGF is shown. B, exdFGFRIIIc is shown. C, an equimolar mixture of C-LYT/aFGF and exdFGFRIIIc is shown. D, an equimolar mixture of C-LYT/aFGF and exdFGFRIIIc is shown as in C, except that 1 ml of a 100 mm 2,5DHPS was injected onto the column (arrow) before raising the choline concentration of the buffer to 150 mm (in C and D, the peak eluted with choline has a long tail only partially shown in the figure). E, shown is the chromatography of an equimolar mixture (∼3.5 nmol) of C-LYT/aFGF and exdFGFRIIIc (containing 5 mm 3-kDa heparin, in the case of the dashed line) using a NaCl gradient (dotted line; except for this NaCl gradient, the other chromatographic conditions are those used in the remainder of the figure). mAU, milliabsorbance units. F, shown is Coomassie Brilliant Blue-stained SDS/PAGE (15%) of the fractions a, b, and c of the chromatograms C and D. The horizontal lines to the left indicate the migration of C-LYT/aFGF (30.8 kDa) and exdFGFRIIIc (38.7 kDa). Chromatography was carried out on 1-ml HiTrapTM DEAE FF columns (GE Healthcare) at a flow rate of 2 ml/min and a pH of 7.5 (Hepes 20 mm, 300 mm NaCl), conditions chosen to avoid any appreciable ionic interaction of FGF-1 (pI 7.9) and exdFGFR2IIIc (pI 5.8), respectively, with the solid phase of the column.