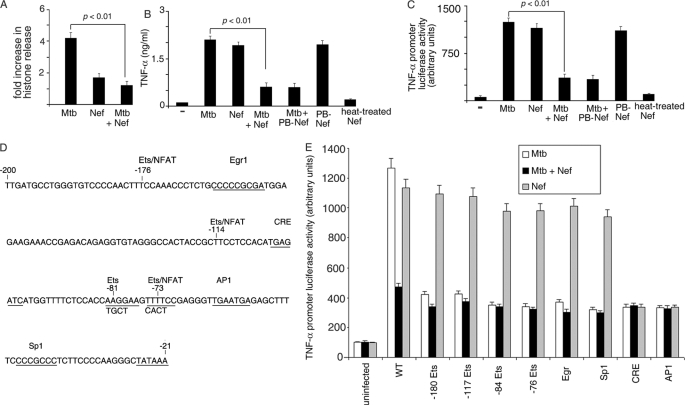
FIGURE 1.
Nef inhibits M. tuberculosis-mediated induction of TNF-α. A, THP-1 cells (in 96-well plates) were left untreated (−) or treated with either M. tuberculosis (Mtb) or Nef or both (Mtb + Nef) for 24 h. Cells were washed and lysed, and cell death was measured using the cell death ELISA kit according to the manufacturer's instructions. B, THP-1 cells (in 96-well plates) were left untreated (−) or treated with either M. tuberculosis (Mtb) or Nef or both (Mtb + Nef). In a separate set of experiments, Nef was pretreated with polymyxin B (PB-Nef) or heated at 95 °C for 10 min (heat-treated) and then used alone or in combination with M. tuberculosis as described above. The release of TNF-α in the supernatant was quantitated by TNF-α ELISA according to the manufacturer's instructions, 24 h after infection. THP-1 cells were transfected with a TNF-α promoter luciferase reporter construct (wt) (C and E) or with mutants devoid of the indicated transcription factor binding sites (E), along with a β-galactosidase expression vector. Cells were then left untreated (− in C), or incubated with either Mtb or Nef or with both (C and E) as indicated. Cells were lysed, and luciferase activities were determined 14 h after infection. The activities were normalized with β-galactosidase activity. Data represent means ± S.D. for three different experiments. D is a diagrammatic representation of the TNF-α promoter indicating the different transcription factor binding sites (underlined). The sequence in the bottom line indicates the mutation by replacement of the corresponding bases on the upper line.