FIGURE 5.
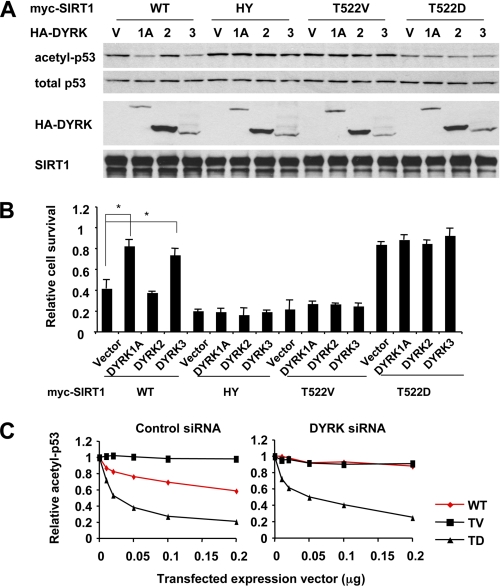
DYRK1A and DYRK3 promote cell survival through phosphorylation of Thr522 residue of SIRT1. A, the SIRT1 T522V mutant fails to mediate DYRK1A and DYRK3-induced deacetylation of p53, whereas the SIRT1 T522D mutant is constitutively active. U2OS cells expressing the indicated proteins were treated with etoposide, and the acetylation of endogenous p53 was analyzed. B, DYRK1A and DYRK3 fail to significantly promote cell survival in SIRT1 T522V-expressing U2OS cells, whereas the SIRT1 T522D mutant constitutively promotes cell survival. U2OS cells transfected with the indicated constructs were treated with etoposide, and 30 h later cell viability was analyzed as described under “Experimental Procedures” (n = 6; *, p < 0.01). C, the SIRT1 T522A mutant is inactive, whereas the SIRT1 T522D mutant is constitutively active regardless of cellular DYRK1A and DYRK3 levels. U2OS cells transfected with control siRNA or siRNA to DYRK1A/3 were transfected with increased doses of vectors for wild-type SIRT1, T522V, or T522D mutants. The acetylation levels of p53 in supplemental Fig. S7 were quantified with the ImageJ program and normalized to the total p53 levels. WT, wild type; HY, H355Y mutant.