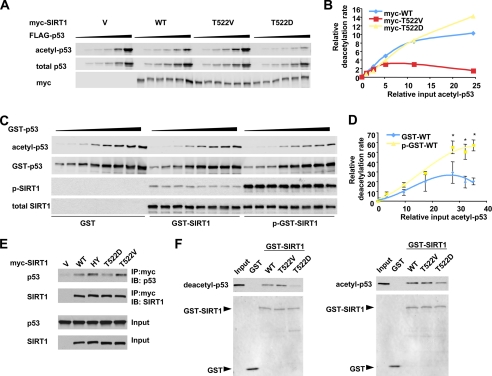
FIGURE 7.
Mechanistic characterization of the effect of Thr522 phosphorylation on the enzymatic behaviors of SIRT1 in vivo and in vitro. A and B, a representative in vivo kinetic analysis of Myc-SIRT1 and phosphorylation mutants. p53-null H1299 cells were co-transfected with 0.125 μg of vectors for Myc-SIRT1 or phosphorylation mutants with increased doses of a construct expressing FLAG-p53 (0, 0.125, 0.25, 0.5, 1, and 2 μg). The cells were then treated with etoposide/MG132 for 1 h, and the acetylated FLAG-p53 and total FLAG-p53 was quantified with the Odyssey Infrared Imaging System (Li-Cor Biosciences) using anti-acetyl-p53 K382 antibodies. C and D, representative in vitro enzymatic analysis of GST-SIRT1 and DYRK1A-phosphorylated GST-SIRT1 proteins. 0.05 μg of purified wild-type SIRT1 (GST-WT) or DYRK1A-phosphorylated wild-type SIRT1 (p-GST-WT) proteins were incubated with 0.15, 0.3, 0.6, 1.2, 1.8, 2.4, 3.0, and 3.6 μg of in vitro acetylated GST-p53 fusion proteins in the presence of 3 mm of NAD+ and 200 nm of trichostatin A and incubated at 30 °C for 1 h. The acetylated GST-p53 was analyzed as described for A (n = 3; *, p < 0.01). E, the SIRT1 T522V mutant displays increased affinity to p53 in cells. HEK293T SIRT1 RNAi cells transfected with indicated expression vectors and then treated with etoposide as described. The cell lysates were then immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-Myc antibodies. F, the SIRT1 T522D mutant displays decreased affinity to deacetylated and acetylated p53 in vitro. Purified GST-SIRT1 and mutants were incubated with purified deacetylated or acetylated FLAG-p53, and SIRT1-associated FLAG-p53 was analyzed by anti-p53 antibodies. WT, wild type; HY, H355Y mutant; IB, immunoblot.