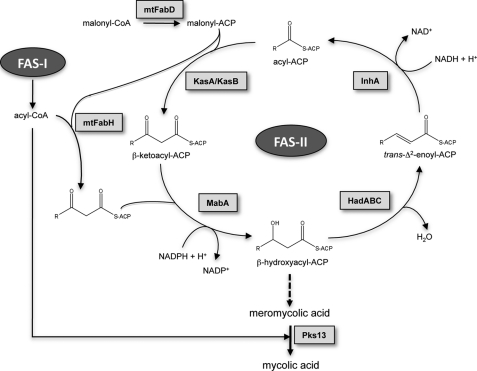
FIGURE 1.
Mycolic acid biosynthetic pathway. The malonyl-CoA:ACP transacylase mtFabD converts malonyl-CoA into malonyl-ACP, providing the elongation building blocks for the FAS-II. Cycles of elongation are initiated by the condensation of the FAS-I acyl-CoA products with malonyl-ACP, a reaction catalyzed by the β-ketoacyl-ACP synthase mtFabH. The second step in the elongation cycle is performed by the NADPH-dependent β-ketoacyl-ACP reductase MabA, generating a β-hydroxyacyl-ACP intermediate, which is subsequently dehydrated by the β-hydroxyacyl-ACP dehydratase HadABC to form a trans-Δ2-enoyl-ACP. The final step in the elongation is carried out by the NADH-dependent enoyl-ACP reductase InhA. Subsequent rounds of elongation are initiated by the elongation condensing enzymes KasA and KasB, giving raise to meromycolic acids, which are condensed with C26 acyl-CoAs by the termination condensing enzyme Pks13 to form mycolic acids.