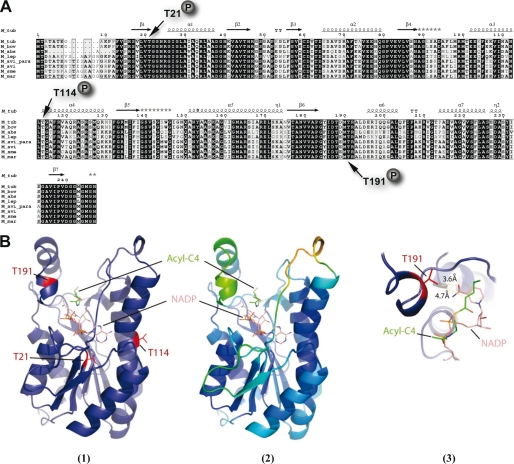
FIGURE 3.
Conservation of phosphoacceptors in MabA orthologues. A, multiple sequence alignment of MabA sequences from various mycobacterial species. The alignment was performed using ClustalW and Espript (M_tub, M. tuberculosis; M_bov, M. bovis; M_abs, M. abcessus; M_lep, Mycobacterium leprae; M. avi_para; Mycobacterium paratuberculosis; M_avi, Mycobacterium avium; M_sme, Mycobacterium smegmatis; M_mar, Mycobacterium marinum). Residues conserved in all species are shown in black boxes. The three phosphorylation sites of MabA_Mtb are indicated. Protein secondary element assignments are represented above the sequences. Numbering of amino acids corresponds to the MabA protein from M. tuberculosis. B, localization of the identified phosphorylation sites in the three-dimensional structure of MabA. (1) MabA in complex with NADPH and the acyl-C4 substrate. The model of the ternary complex MabA-cofactor-substrate was obtain after superposition of the crystal structure of MabA with different homologous ternary complexes. The three phosphorylation sites identified by mass spectrometry are represented in red. (2) The same complex has been redrawn with the color representing crystal structure B factor of the MabA holo-form (PDB code 1UZM). The residues with the lower B factor and mobility are represented in blue, whereas those with the higher B factor and mobility are in green and yellow. Only Thr191 lies in a high mobility zone and probably accessible to the kinase. (3) Close-up of the substrate and cofactor binding pocket centered on residue Thr191. The lateral chain of Thr191 is 4.7 Å from the substrate and 3.6 Å from the cofactor. Addition of the phospho group on the oxygen of the lateral chain of Thr191 of MabA is incompatible with substrate binding.