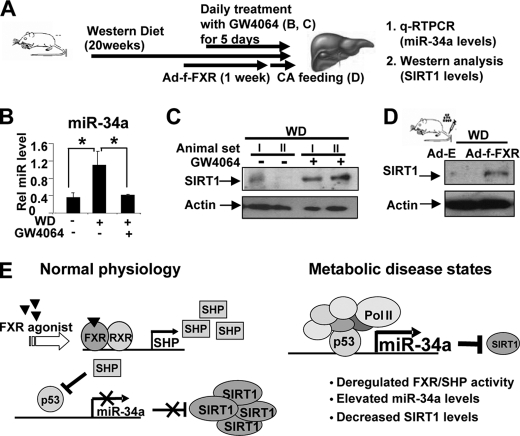
FIGURE 5.
Activation of FXR decreased miR-34a levels and increased SIRT1 protein levels in diet-induced obese mice. A, experimental outline is shown. B and C, mice fed WD chow were treated daily with GW4064 for 5 days, and hepatic miR-34a levels (B) and SIRT1 protein levels (C) were measured. D, mice fed WD chow were injected with Ad-FLAG-FXR, and 1 week later, mice were fed 0.5% cholic acid-chow for 6 h; hepatic SIRT1 protein levels were measured. E, a proposed model for FXR/SHP/miR-34a regulatory network controlling hepatic SIRT1 levels is shown. In this model, miR-34a inhibits translation of hepatic SIRT1 by binding to the 3′-UTR of SIRT1 transcript with partial base pairing. In normal mice, activation of FXR induces expression of SHP, which suppresses transcription of the miR-34a gene by inhibiting p53 binding to the miR-34a promoter. In contrast, in diet-induced obese mice, the FXR/SHP pathway is defective, which results in elevated miR-34a levels and subsequently decreased SIRT1 protein levels in the liver.