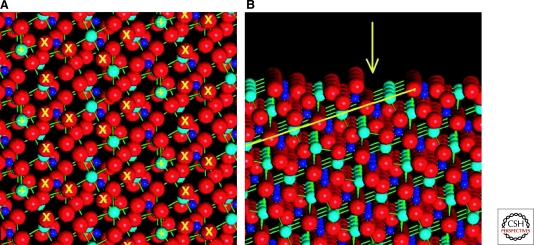
Figure 2.
The common calcite form of CaCO3 often displays chiral surfaces. (A) The structure of the (21–34) face of calcite features a chiral arrangement of positive (+) and negative (X) charge centers near the crystal termination. Ca, C, and O atoms are turquoise, blue, and red, respectively. In this 20 × 20 Å view the (01–8) axis is vertical—an orientation that provides a useful image of the surface structure. (B) A view of this surface tilted 3° from horizontal (projected almost down the [01–8] axis) reveals the irregular surface topology, including 2-Å-deep steps (yellow arrow) that result from the oblique intersection of layers of Ca and rigid CO3 groups with the surface (yellow line).