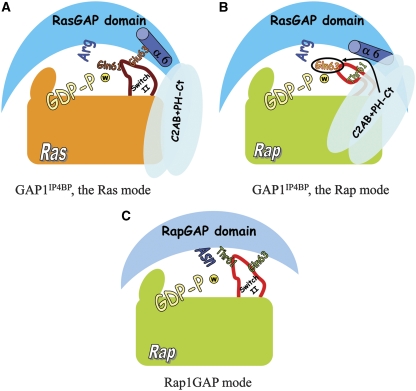
Figure 6.
A schematic model of the different catalysis modes of GAP1IP4BP (blue) with Ras (orange) or Rap (green). In the Ras mode (A) the C2AB and PH-Ct domains are not implicated in catalysis, and switch-II (dark red) is in the conventional RasGAP mode, with Gln61 pointing towards the nucleophilic water molecule (w, yellow sphere) and the γ-phosphate. In the Rap mode (B), the extra domains of GAP and helix-α6 with Pro489 induce a conformational change of the switch-II of Rap (red), allowing Gln63 to act as the catalytic residue. (C) In RapGAP-mediated catalysis on Rap, the Asn thumb inserts into the active site to adopt the role of the intrinsic Gln.