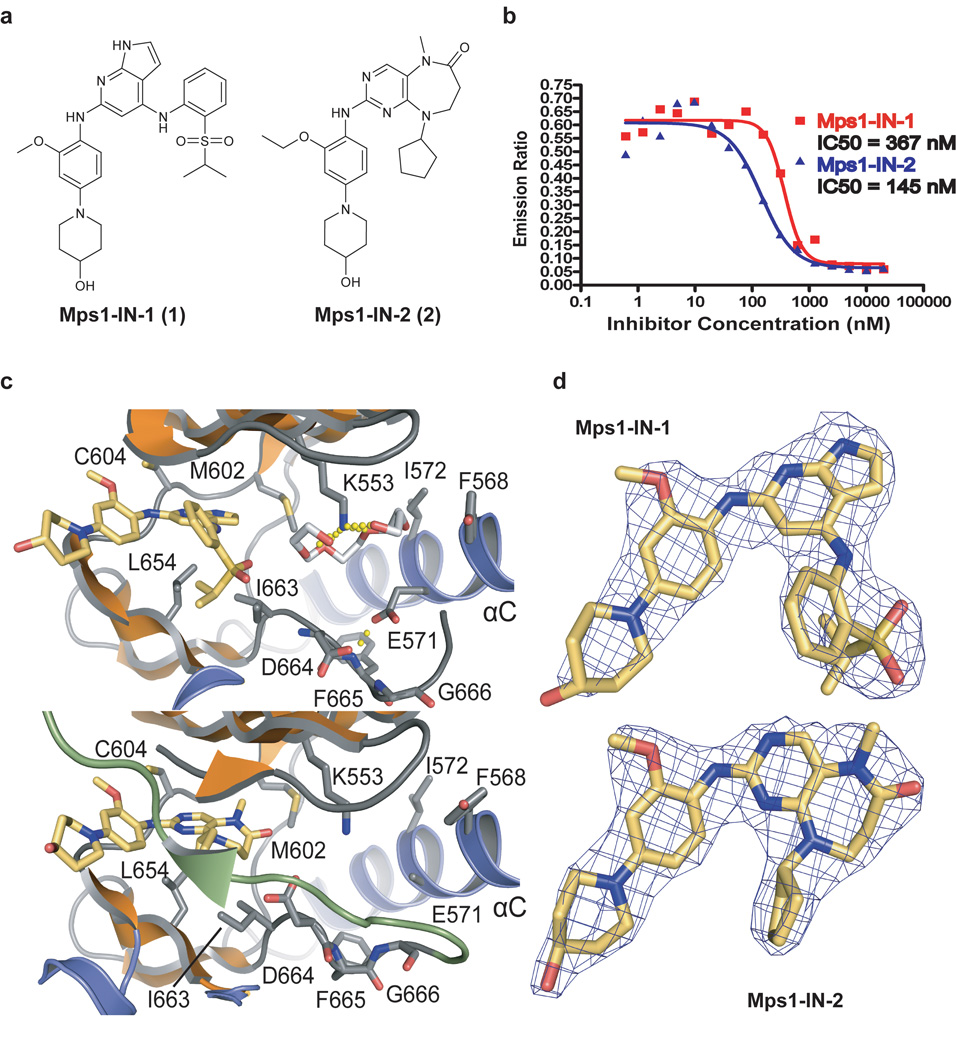
Figure 1. Mps1-IN-1 and Mps1-IN-2 inhibit Mps1 kinase activity and bind Mps1 in the ATP-binding site.
(a) The chemical structures of two ATP-competitive Mps1 kinase inhibitors, Mps1-IN-1 and Mps1-IN-2, are derived from two scaffold series: pyrrolopyridine and pyrimidodiazepinone respectively. (b) In vitro kinase assays using the Lanthascreen technology were performed to assess the in vitro activity of compounds 1 and 2. 5 µg/mL Mps1 (∼ 40 nM) kinase were used in each reaction with 1 µM ATP (Km,app < 1 uM) and 200 nM AF-647 E4Y substrate. (c) Active site of Mps1 in complex with Mps1-IN-1 (upper panel) and the methoxy derivative of Mps1-IN-2 (methoxy-Mps1-IN-2 - lower panel). The most important residues interacting with the inhibitor are shown in stick representation and are labeled. The polyethylene glycol molecule coordinating the conserved active site lysine (K553) in the Mps1-IN-1 complex is also shown. Carbon atoms of Mps1-IN-1 and Mps1-IN-2 are shown in yellow to discriminate from Mps1 kinase residue side chains. (d) 2FoFc electron density map contoured at 2σ around the inhibitor molecules.