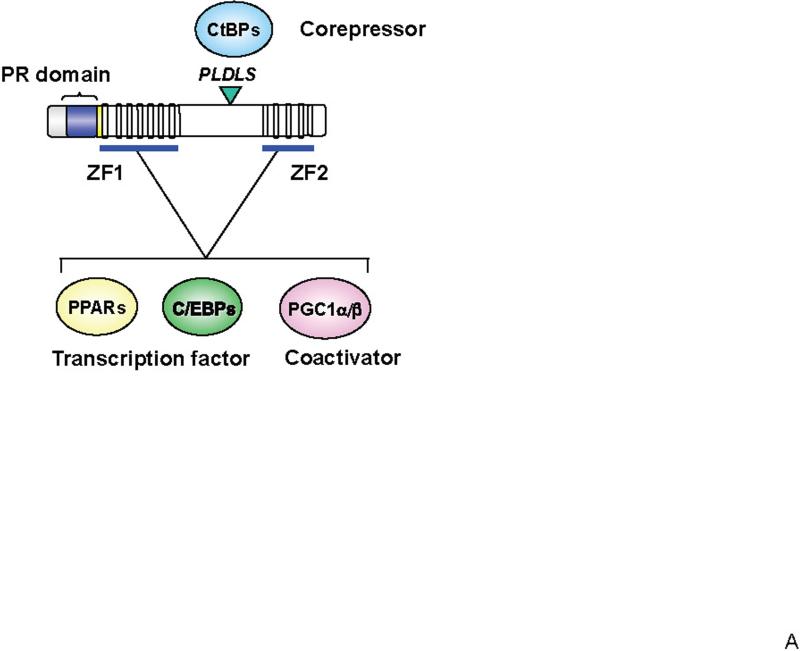
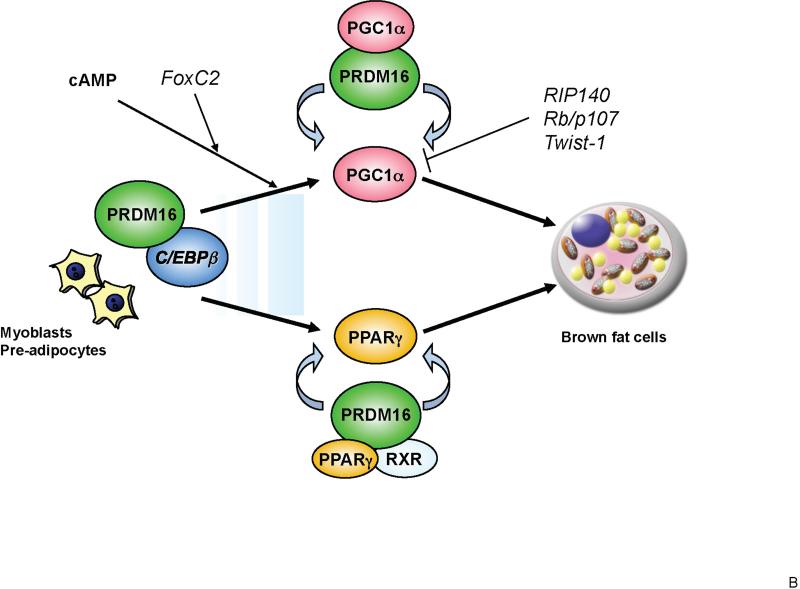
Figure 1. Transcriptional control of brown fat development through PRDM16.
(A) Structure of PRDM16 and key domains of its function. PRDM16 directly interacts with canonical transcription factors such as PPARα, PPARγ and C/EBP family members and transcriptional co-activators PGC-1α and PGC-1β through the two sets of zinc finger domains (ZF1 and ZF2). PRDM16 is also associated with the co-repressors CtBP1 and 2 through its PLDLS motif. This interaction mediates the repressive action of PRDM16 on the expression of white fat cell-specific genes. (B) PRDM16-C/EBP-β transcriptional complex acts in myf5-positive myoblastic precursors or pre-adipocytes to induce the expression of PPARγ and PGC-1α. PRDM16 co-activates PPARγ and PGC-1α, which then drives a brown fat differentiation program. The cAMP-dependent thermogenic gene program is potentiated by FoxC2 and PRDM16. RIP140, Rb/p107, and Twist-1 antagonize the expression or transcriptional activity of PGC-1α and repress brown fat genetic program.