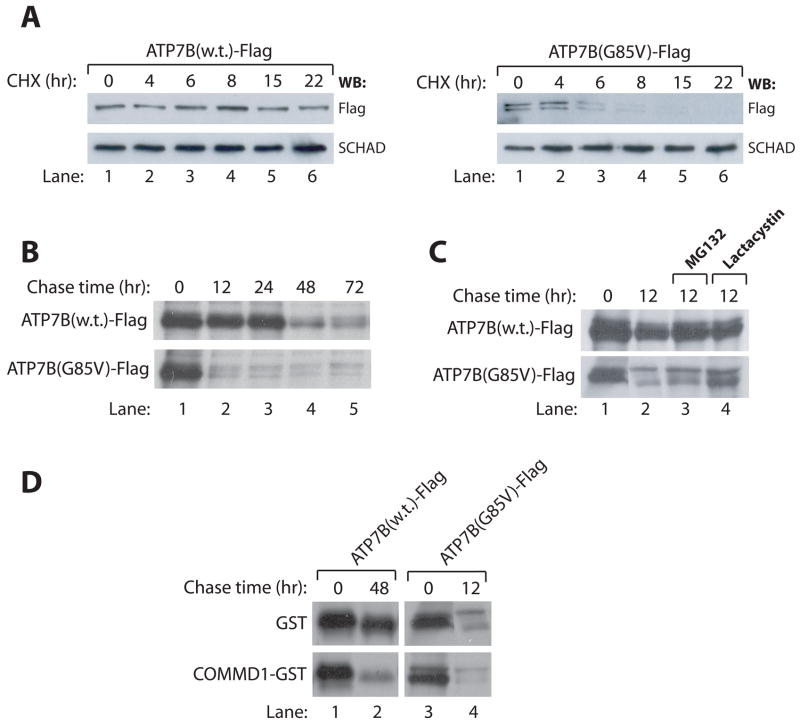
Figure 7. ATP7B-G85V is subject to increased degradation, partially facilitated by COMMD1.
A: HEK293T cells were transfected with cDNA constructs encoding for ATP7B-Flag or ATP7B-G85V-Flag and subsequently incubated with cycloheximide for the indicated time intervals. Cell lysates were generated and analyzed for expression of ATP7B-Flag and ATP7B-G85V-Flag. Equal loading was confirmed by immunoblotting for SCHAD.
B: HEK293T cells were transfected with cDNA constructs encoding for ATP7B-Flag or ATP7B-G85V-Flag and biosynthetically labeled with 35S-labeled methionine and cysteine for 90 minutes. After labeling, cells were chased with cold medium for the indicated time intervals. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-Flag affinity gel before analysis by SDS-PAGE. Proteins were visualized with fluorography.
C. HEK293T cells expressing ATP7B-Flag or ATP7B-G85V-Flag were subjected to biosynthetic labeling and immunoprecipitation as described in B. During 12 hr chase with cold media, cells were incubated with the proteasome inhibitors MG132 or Lactacystin as indicated.
D. HEK293T cells expressing ATP7B-Flag or ATP7B-G85V-Flag together with GST or COMMD1-GST were subjected to biosynthetic labeling and immunoprecipitation as described in B.