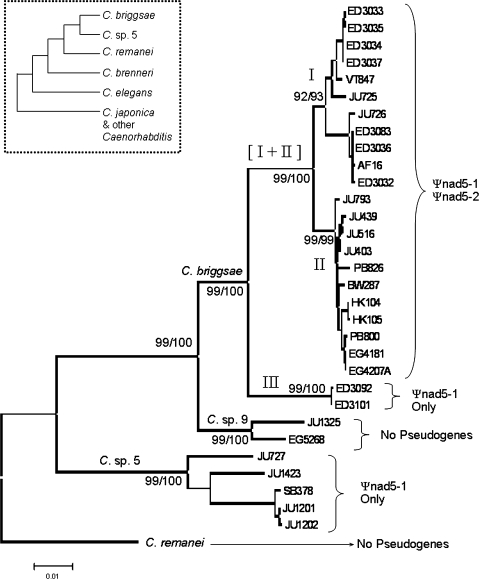
FIG. 2.
Presence and absence of mtDNA pseudogenes in Caenorhabditis. Main display is an NJ phylogram for Caenorhabditis briggsae, Caenorhabditis sp. 9, Caenorhabditis sp. 5, and C. remanei using 1,995 bp of mtDNA sequence. All gene sequences amplified for this study were used though pseudogene sequences were excluded so that their presence/absence could be independently mapped onto the phylogeny. The presence/absence of Ψnad5-1 and Ψnad5-2 in different species and intraspecific clades of C. briggsae is indicated on the right. Bootstrap values for maximum parsimony (left) and NJ (right) methods (1,000 replicates performed for each) are indicated to the left of the corresponding node. Scale bar shows 0.01 substitutions per site. The cladogram in the dashed box on the top left shows evolutionary relationships in the Elegans clade of Caenorhabditis nematodes based on nuclear DNA data (Kiontke et al. 2007).