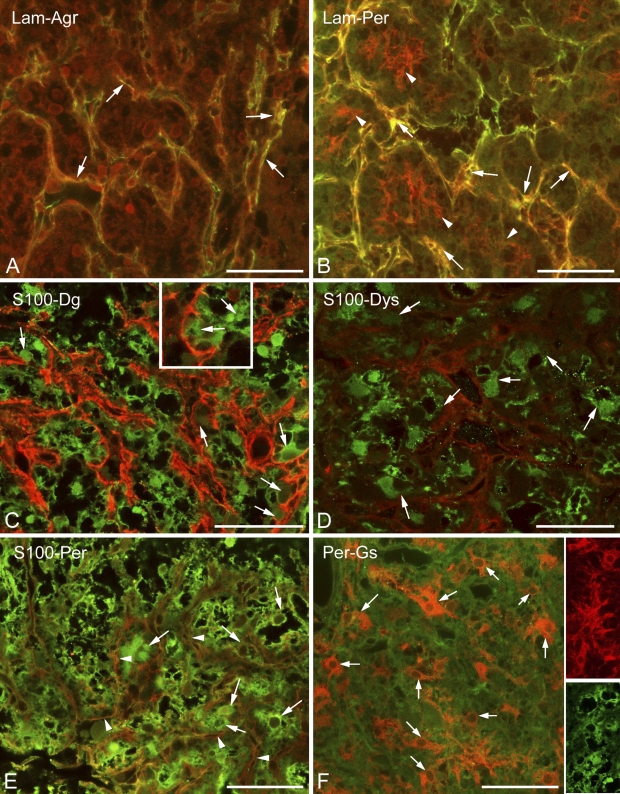
Figure 2.
Basal lamina and dystroglycan–dystrophin complex in the neurohypophysis; relationship to cells. (A) Agrin (red) colocalizes (arrows, yellow) with laminin (green) along the “septa.” (B) Perlecan (red) colocalizes (arrows, yellow) with laminin (green) along the “septa” but also forms a finer mesh (arrowheads, red) within the holes of the laminin network. (C) S100 (green) and β-dystroglycan (red). S100-immunopositive cells (arrows) seem to form the β-dystroglycan layer. (D) Dystrophin (red) around S100-immunopositive cells (arrows, green). The scattered immunoreactive, green punctae in the background are artifacts. (E) Perlecan (arrowheads, red) mesh around S100-immunoreactive cells (arrows, green). Note the similar patterns in C and D. (F) Perlecan (here, green) mesh around glutamine synthetase-immunopositive cells (arrows, red). Note differences between the shapes of glutamine synthetase-positive cells (red) and those of S100-positive cells (green) in the insets. These two inset images are taken from different reactions. Agr, agrin; Lam, laminin; Per, perlecan; Gs, glutamine synthetase. Bars: A–F and insets in F = 50 μm; inset in C = 25 μm.