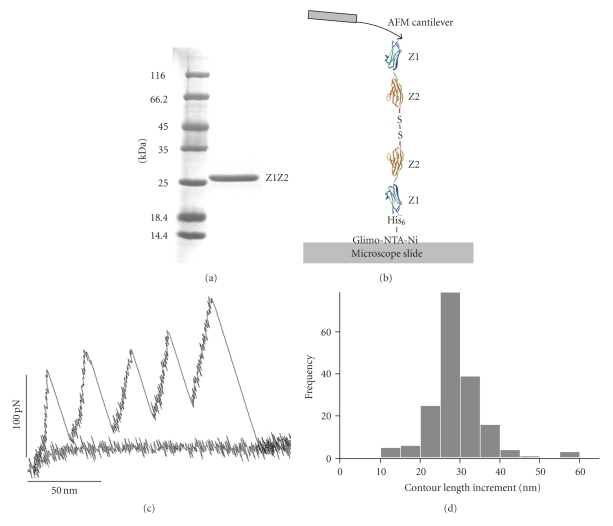
Figure 2.
(a) SDS-polyacrylamide electrophoretogram of the recombinant Z1Z2 fragment. (b) Nanomechanical manipulation of the Z1Z2 chemical dimer. The molecular design of the Z1Z2 chemical dimer is indicated. Two recombinant Z1Z2 modules, each with a His6-tag at its N-terminus and a cysteine at its C-terminus, respectively, are dimerized via a disulphide bond under oxidizing conditions. The dimer is manipulated by using single-molecule AFM. (c) Force versus end-to-end length curve of a Z1Z2 dimer. The first four sawtooth peaks correspond to the unfolding of each of the four domains (two Z1 and two Z2), and the fifth peak corresponds to the final dissociation of the complex from either the AFM tip or the substrate surface. (d) Distribution of contour-length gain during the sawtooth force transitions. Average contour-length gain per transition was 29.1 ± 0.6 nm (±SEM).