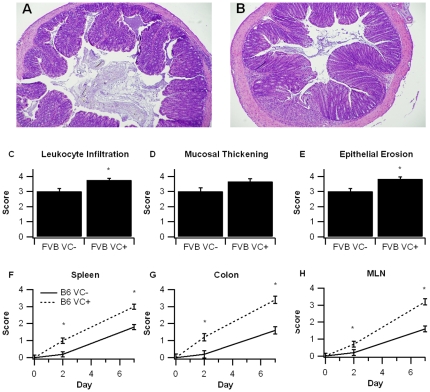
Figure 3. Effect of intestinal epithelial cell-specific PPAR γ deletion on colon histopathology and inflammation.
PPAR γ flfl; Villin Cre+ (VC+) or PPAR γ flfl; Villin Cre- (VC-) mice with a mixed FVB/C57BL6/J (FVB) or C57BL6/J (B6) background were treated with 2.5% dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) or water (no DSS) for 7 days. Representative photomicrographs of colonic samples from VC- (A) and VC+ (B) FVB mice with DSS colitis (Original magnification, 40×). Colonic specimens from FVB mice underwent blinded histological examination and were scored (1–4) on leukocyte infiltration (C), and mucosal wall thickening (D), and epithelial erosion (E) on day 7 of the challenge. In B6 mice spleen (F), colon (G), and mesenteric lymph nodes MLN (H) were scored based on macroscopic signs of inflammation on days 2 and 7. Data are represented as mean ± standard error. Points with an asterisk are significantly different (P<0.05).