Fig. 6.
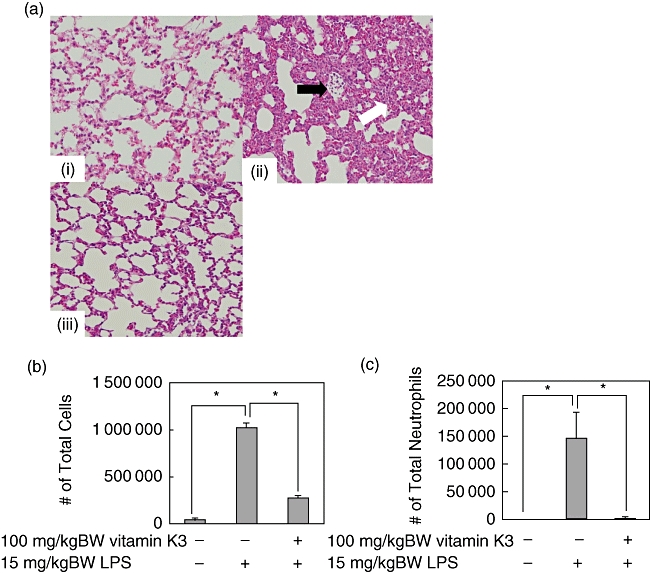
Therapeutic effects of vitamin K3 in the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) mouse model. Male C57BL/6 mice were injected intraperitoneally with 15 mg/kg body weight (BW) LPS or saline as a vehicle control. After 30 min, the mice were injected intraperitoneally with 100 mg/kg BW vitamin K3 or corn oil as vehicle control. (a) After 6 h the mice were killed, and the lung tissue was collected. The lung tissue was stained with haematoxylin & eosin (H&E ×400), and histopathological examination of the lung tissue was performed. Typical pictures are shown from at least triplicate determinations. (i) Negative control group; (ii) LPS group; (iii) LPS+vitamin K3 group. The white arrow indicates oedematous change in the alveolar wall and the swelling of alveolar epithelial cells, and the black arrow indicates massive polymorphonuclear infiltration. (b,c). After 24 h the mice were killed, and total cell (b) and neutrophil (c) counts in the bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid were performed. Each data value is expressed as mean ± standard error, n = 3. The presence of significant differences is indicated by asterisks (P < 0·05).
