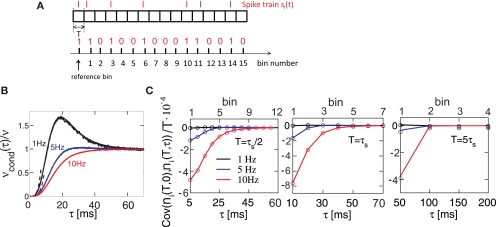
Figure 4.
Spike correlations and count correlations within a spike train. (A) Example of a binned spike train si(t), bins numbered with respect to a reference time bin. (B) νcond(τ) vs. τ for τ = 10 ms, numerical solution and simulations for the firing rates ν = 1 Hz (black), 5 Hz (blue) and ν = 10 Hz (red) are superimposed. Dotted lines denote the corresponding solutions for small τ (Eq. 23). (C) Cov(ni(T,0),nj(T,τ))/T vs. τ for τs = 10 ms, time bin T = τs/2 = 5 ms (left), T = 10 ms = τs (middle), T = 5τs = 50 ms (right). Circles denote the corresponding simulation points, adjacent time bins are denoted by the first points on the time axis. All spike correlations are computed for C(τ) as in Eq. 13.