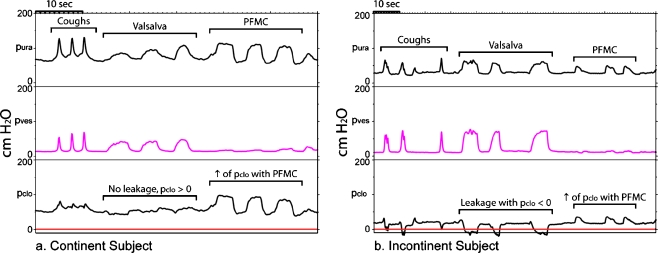
Fig. 2.
a Typical signals from a continent subject. p ura and p ves are measured using the urethral sleeve sensor. p clo is the subtracted value of p ves from p ura. All pressures are expressed in centimeters of water on the y-axis. Time is on the x-axis. During Valsalva, the continent subject increases her abdominal pressure and vesical pressure (p ves), and there is a corresponding increase in urethral pressure (p ura). The subject is able to maintain p clo > 0, and no leakage is observed. During PFMC, the continent patient is able to increase her p clo pressures by increasing her p ura. This subject is clearly performing the PFMC correctly because there is no increase in p ves. p ura urethral pressure, p ves vesical pressure, p clo urethral closure pressure, PFMC pelvic floor muscle contraction. b Typical signals from an incontinent subject. During Valsalva, the incontinent subject is unable to maintain her urethral closure pressures when vesical pressure increases and p clo becomes <0 cm H2O, resulting in urine leakage. Even in the incontinent subject there is a modest increase in p clo during a properly performed PFMC