Figure 3.
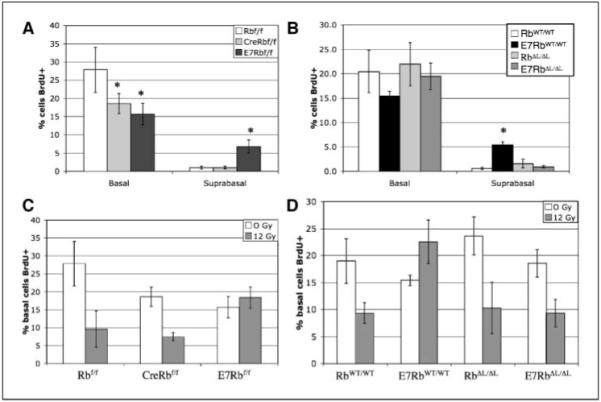
Quantitative effects on DNA synthesis. Basal and suprabasal cells from BrdUrd-stained cervical epithelia were counted as BrdUrd positive or BrdUrd negative, and the frequency of BrdUrd-positive cells was graphed. A, BrdUrd incorporation in Rbflox mice. *, P < 0.05, statistically significant change compared with Rbflox/flox. B, BrdUrd incorporation in RbWT and RbΔL mice. *, P < 0.05, statistically significant increase in suprabasal DNA synthesis in K14E7RbWT/WT mice compared with all other genotypes. C, E7 expression, but not Rb inactivation, prevents DNA damage–induced cell cycle arrest. Mice were exposed to 0 or 12 Gy ionizing radiation 24 hours before BrdUrd administration. BrdUrd staining frequency in basal cells is graphed. BrdUrd incorporation frequency is significantly reduced in irradiated Rbflox/flox and K14CreRbflox/flox mice versus unirradiated mice (P < 0.05). D, pRb inactivation is necessary for E7 to disrupt DNA damage–induced arrest. Mice were irradiated and analyzed as in (C). BrdUrd incorporation frequency is significantly reduced in irradiated RbWT/WT, RbΔL/ΔL, and K14E7RbΔL/ΔL mice versus unirradiated mice (P < 0.05).
