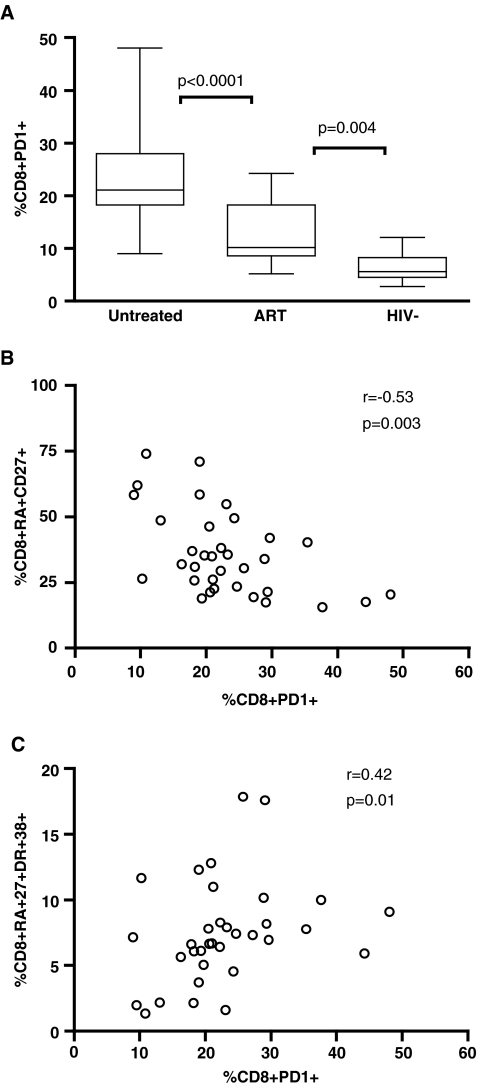
FIG. 4.
PD-1 expression on CD8+ T cells is higher in HIV-positive children. Dead cells were first gated out using a violet excited viability dye (LIVE/DEAD Fixable Dead Cell Stain; Invitrogen). Samples were subsequently gated on the CD3+/CD8+ lymphocyte population then the percent of PD-1-positive cells was determined. Gating was standardized and set using the fluorescence minus one (FMO) control for PD-1. (A) PD-1 expression on CD8+ T cells was highest in children not receiving ART (p < 0.0001). Viral suppression does not lead to normalization of PD-1 expression compared to samples from HIV-negative children (p = 0.004). (B) The presence of PD-1 expression negatively correlated with the frequency of naive CD8+ T cells (r = −0.53, p = 0.003) and (C) positively associated with naive CD8+ T cell activation (r = 0.42, p = 0.01).