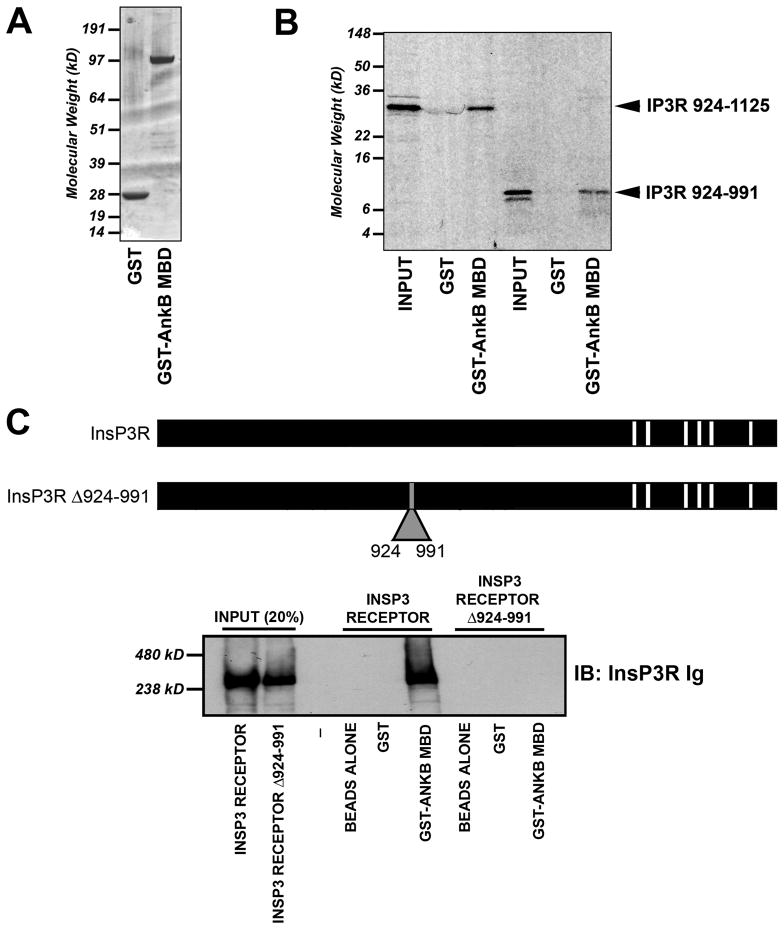
Figure 5. InsP3 receptor residues 924–991 are required and sufficient for ankyrin-B association.
A, Coomassie Blue stained gel depicting purified GST and GST-ankyrin-B (10 μg of each protein) membrane-binding domain (InsP3 receptor binding domain on ankyrin-B). B, InsP3 receptor residues 924–991 are sufficient to mediate interaction of InsP3 receptor with ankyrin-B membrane-binding domain. Constructs shown in Figure 3 and 5 were inserted into pcDNA3.1(+) and in vitro transcribed/translated in the presence of 35S-methionine. Products were used in binding experiments with purified GST or GST-ankyrin-B membrane-binding domain. Shown are representative experiments from two radiolabeled N-terminal samples including 924–991 and 924–1125. We observed no binding of InsP3 receptor constructs with GST alone. C, Full-length InsP3 receptor Δ924–991 lacks ankyrin-B-binding activity. Full-length InsP3 receptor and InsP3 receptor Δ924–991 were generated using baculovirus (Sf21 cells) and individually incubated with GST-ankyrin-B membrane-binding domain immobilized on glutathione sepharose. Bound protein was eluted and analyzed by immunoblot using affinity-purified InsP3 receptor Ig (generated against InsP3 receptor C-terminal domain). Input equals 20%.