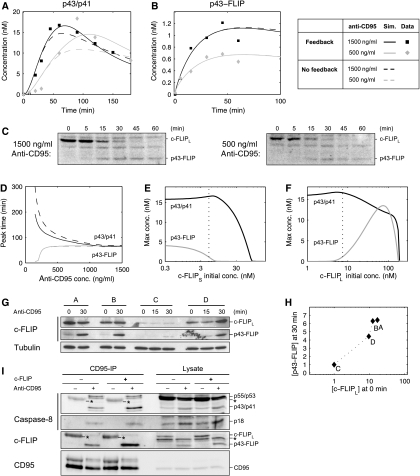
Figure 7.
c-FLIPL recruitment kinetics explains the differential dynamics of the two pathways. (A) Simulation and experimental data of p43/p41 dynamics for 1500 and 500 ng/ml of stimulating anti-CD95 antibody. (B) Same as (A) for p43-FLIP. The data points were obtained by quantifying the blots shown in (C). (C) HeLa-CD95 cells stimulated with 1500/500 ng/ml anti-CD95 for the indicated time points. Lysates were used for western blots analysis using an antibody against c-FLIP. The full-length form of c-FLIPL and its cleavage product p43-FLIP are indicated. (D) The curves show the time when p43/p41 and p43-FLIP reached their peak level in the simulation as a function of the antibody concentration. (E) Model prediction of the maximal concentration of p43/p41 and p43-FLIP depending on the initial concentration of c-FLIPS. The dotted line indicates the estimated level of c-FLIPS in our setting. Stimulation intensity corresponds to 1000 ng/ml of anti-CD95 antibodies. (F) Same as in (E) but with c-FLIPL. (G) Western blotting of four different clones of HeLa-CD95 cells stably overexpressing c-FLIPL in different amounts. Western blots show the full-length form of c-FLIPL and its cleavage product p43-FLIP after induction with 1000 ng/ml of anti-CD95 for the indicated time points. Tubulin serves as a loading control. (H) Quantification of (G) by plotting the intensity of c-FLIPL at 0 min against p43-FLIP at 30 min. For normalization, the amounts of c-FLIPL and p43-FLIP in clone C were set to 1, as they exhibited the lowest levels. (I) HeLa-CD95 cells with a stable c-FLIP downregulation (c-FLIP−) and control-transfected HeLa-CD95 cells (c-FLIP+) were generated by RNA interference. The cells were kept under nonstimulated conditions for control (anti-CD95−) or stimulated with 500 ng/ml anti-CD95 for 30 min (anti-CD95+). The CD95-IP was performed using anti-CD95 antibodies. The immunoprecipitated proteins (CD95-IP) and the lysates were analyzed by western blot using antibodies against caspase-8, c-FLIP and CD95. Secondary antibodies recognize the heavy chain (50 kDa) of the antibody used for the IPs. Thus, the heavy chain of the antibody used for immunoprecipitation is marked in the western blot with an asteric (*=IgGH). Importantly, the amount of antibody in the unstimulated lane was always higher as it was added after cell lysis.