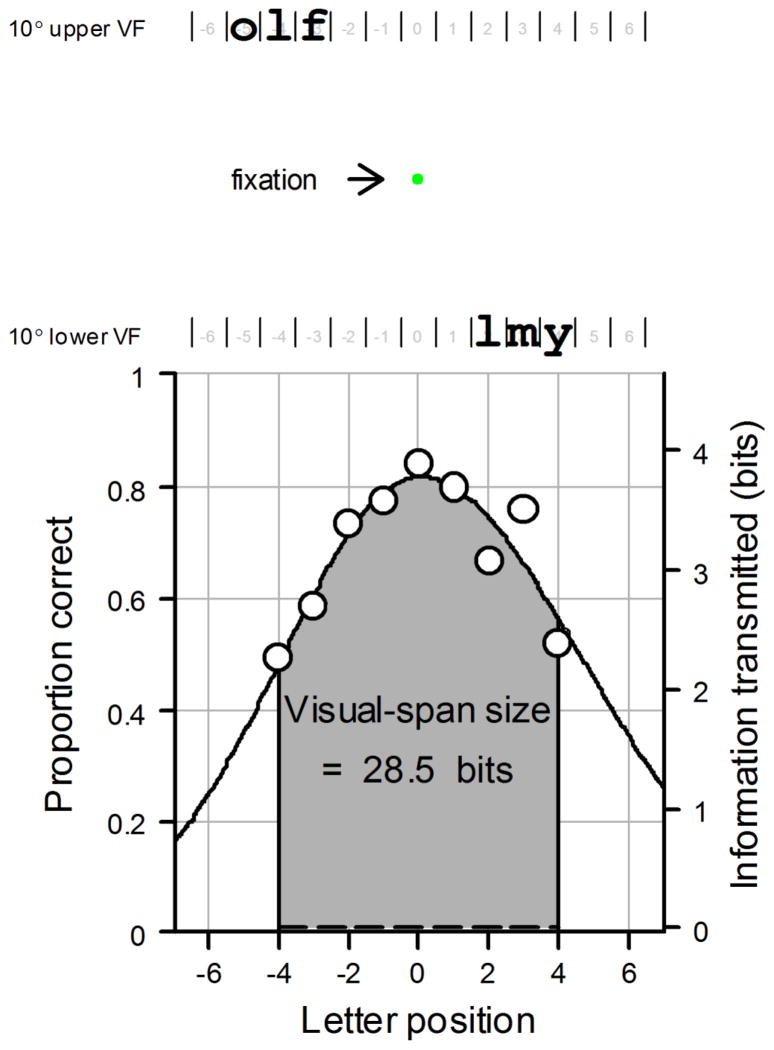
Figure 1.
Example of a visual-span profile. In a visual-span profile, letter-recognition accuracy (proportion correct) is plotted against letter position left or right of the midline. Letter-recognition accuracy is measured with trigram stimuli, random strings of three letters. In this example, the trigram for the lower visual field (VF) presentation, “lmy”, is at letter position +3, indicating that the middle letter of the trigram is located at 3 letter positions to the right of the midline. The trigram for the upper VF, “olf”, is at letter position −4. Letter-recognition accuracy is calculated by accumulating data from multiple trigram trials at each letter position. Proportion correct for letter recognition at each letter position is converted into information transmitted in bits. The area under the visual span indicates the visual-span size. Using letter positions −4 to +4, the visual span in this figure transmits 28.5 bits of information. In the current study, subjects fixated on a green dot 10° above or below letter position 0.