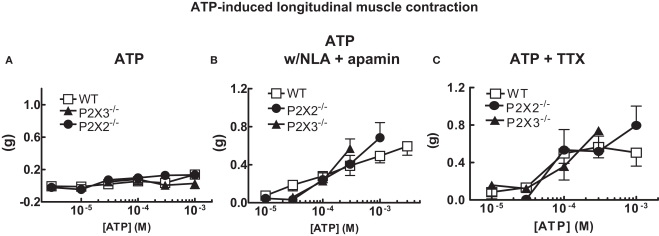
Figure 2.
ATP induced longitudinal muscle contractions in the mouse colon. (A) ATP does not change the resting tone of longitudinal muscle in colonic segments from WT (n = 14) and P2X2 (n = 7) and P2X3 (n = 12) subunit KO mice. (B). ATP caused longitudinal muscle contractions in colonic segments of WT (n = 8) and P2X2 (n = 7) and P2X3 (n = 4) subunit KO mice when NLA (100 μM) and apamin (0.1 μM) were added to the Krebs’ solution. (C) ATP-induced contractions (NLA and apamin present) were not blocked by TTX (0.3 μM) in colonic segments of WT (n = 9) and P2X2 (n = 6) and P2X3 (n = 3) subunit KO mice. Data are mean ± SEM. In all of these studies there were no differences between responses obtained in tissues from WT, P2X2 and P2X3 subunit KO mice (two-way ANOVA, P > 0.05).