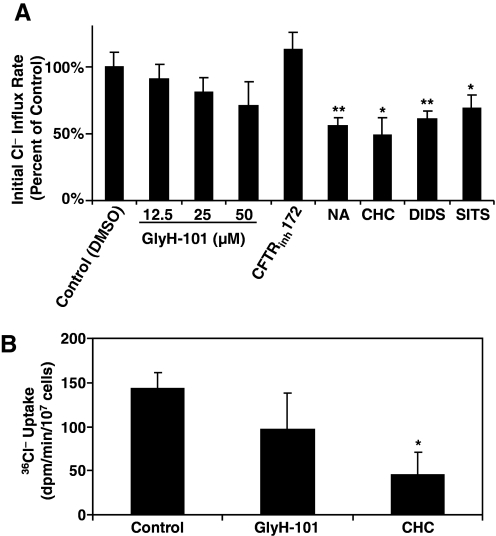
Figure 3.
Effects of chloride or anion channel inhibitors on the initial rate of chloride uptake to the cytosol of zymosan-activated normal neutrophils. (A) Effects of chloride or anion channel inhibitors on the initial rate of chloride uptake to the cytosol of zymosan-activated neutrophils by colorimetric assay. Neutrophils, depleted of chloride by incubation in the NaGlu R for 1 h at 4°C, were allowed to phagocytose opsonized zymosan particles for 15 min at 37°C. The cells were then incubated with the stated concentrations of channel inhibitors in 135 mM NaCl R for 2, 5, and 10 min. Samples in triplicate were collected at each time-point and assayed for the total chloride content with a colorimetric assay as described in Materials and Methods. The initial rate of chloride uptake for each condition was calculated and compared with that of the DMSO control. The final concentration(s) for each inhibitor were GlyH-101 (CFTRinh, 12.5 μM, 25 μM, and 50 μM), CFTRinh172 (CFTRinh, 20 μM), NA (100 μM), CHC (10 mM), DIDS (100 μM), and SITS (100 μM). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. (B) Effects of chloride or anion channel inhibitors on the initial rate of radioactive 36Cl uptake to the cytosol of zymosan-activated neutrophils, which from five donors, similarly depleted of chloride, were allowed to phagocytose opsonized zymosan particles for 15 min at 37°C. The cells were then incubated with the stated concentrations of channel inhibitors in 135 mM chloride buffer containing radioactive 36Cl− (1.5 μCi/ml) for 2, 5, and 10 min. Then, the cells were assayed for 36Cl− uptake. The initial rates were determined from kinetic plots over a 10-min period. *, P < 0.05, compared with the control group (n=5).