Fig. 4.
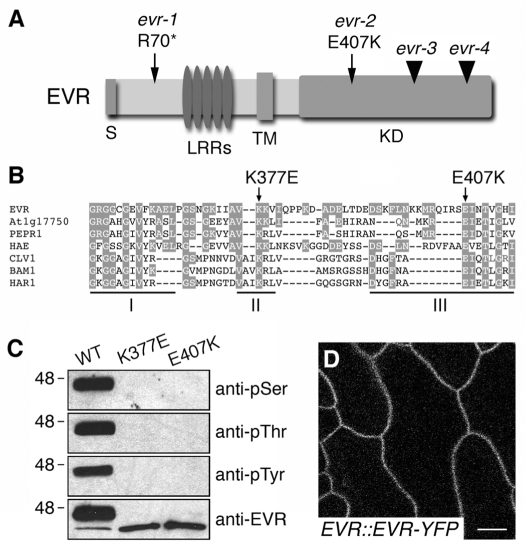
EVR encodes a membrane-localized LRR-RLK. (A) Diagram of the EVR protein, with the sites of the identified evr mutations indicated. The regions corresponding to the signal peptide (S), leucine-rich repeats (LRRs), transmembrane domain (TM) and kinase domain (KD) are indicated. Point mutations are marked by arrows, and T-DNA insertions by arrowheads. (B) Sequence alignment of kinase subdomains I-III from EVR and related LRR-RLKs from Arabidopsis and Lotus japonicus. Amino acids conserved between EVR and other proteins are shaded. The sites of the conserved glutamic acid in subdomain III affected by the evr-2 mutation and an invariant lysine in subdomain II required for kinase activity are marked by arrows above the alignment. (C) The recombinant EVR KD autophosphorylates at serine, threonine and tyrosine residues in vitro. Mutations in subdomains II (K377E) and III (E407K) of the kinase domain block the kinase activity of EVR. EVR antiserum recognizes ~46 and ~40 kDa phosphorylated and unphosphorylated proteins, respectively. (D) EVR localizes to the plasma membrane. Fluorescent localization of the EVR-YFP marker in epidermal cells of wild-type leaf petioles (stems). Scale bar: 10 μm.