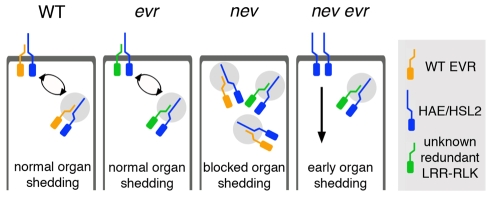
Fig. 9.
A model for EVR function during the transition to floral organ separation. In wild-type AZ cells before organ shedding, EVR might inhibit cell separation by interacting with ligand-binding LRR-RLKs, such as HAE/HSL2, that trigger cell wall loosening and separation. This interaction could promote the internalization and recycling of inactive receptor complexes through the endosomal system. Continued signaling from a ligand-activated HAE/HSL2 complex would lead to organ shedding in older flowers. The EVR RLK may act redundantly with another LRR-RLK(s), such that loss of EVR alone would not alter the timing of abscission. Disrupting NEV activity might alter the trafficking of receptor complexes containing EVR or EVR-like RLKs, thereby blocking a signal required for cell separation. Mutations in EVR could bypass the requirement for NEV in floral organ shedding, resulting in constitutive signaling of the HAE/HSL2 LRR-RLKs, premature activation of organ separation, the enlargement of AZ regions, and deregulated AZ cell expansion.