Figure 1. Examination of the interaction between LRBP-Gal4 BD (binding domain) and prey-Gal4 AD (activation domain) by yeast mating assay.
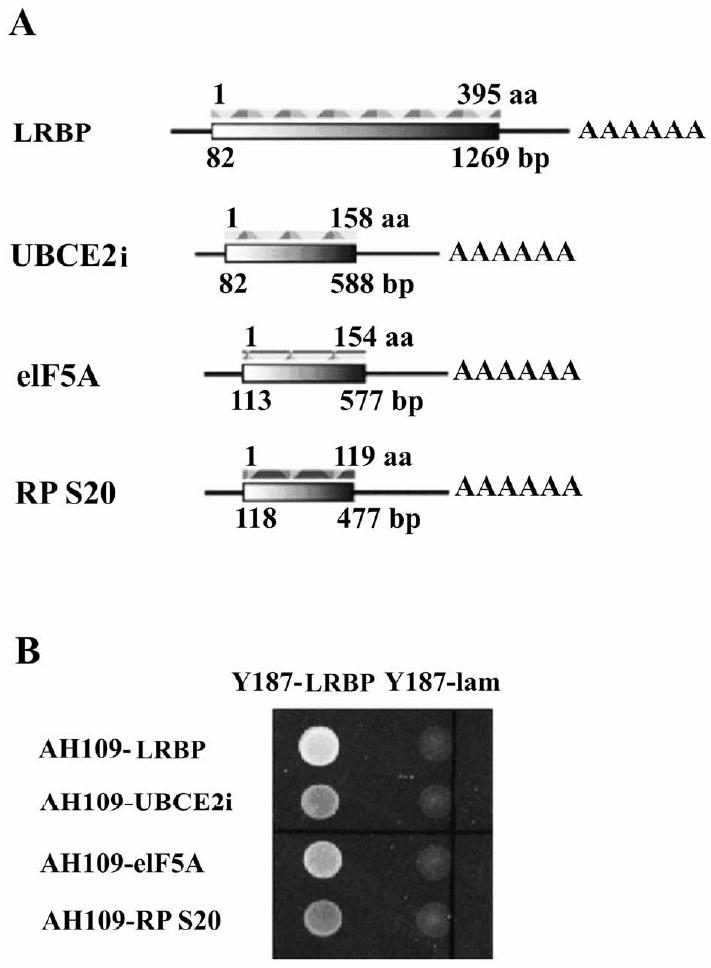
(A) Schematic representation of rat LRBP (fused in frame to the Gal4 BD sequence in plasmid pGBKT7) and prey proteins (fused in frame to the Gal4 AD sequence in plasmid pGADT7).
(B) The complete coding regions of UBCE2i, eIF5A and RPS20 were cloned and fused in frame to the Gal4 AD sequence in plasmid pGADT7 and the plasmids were transformed into AH109 yeast strain. Rat LRBP was fused to the Gal4 BD sequence in plasmid pGBKT7 and the plasmid was transformed into Y187 yeast strain. Protein-protein interactions were evaluated by mating transformed AH109 and Y187 yeasts and examining the growth on SD-WHL plates (lacking tryptophan, leucine and histidine). The presence of both plasmids in mated yeasts was verified by growth on SD-WL plates (not shown). LRBP-LRBP interaction was used as a positive control. Lamin was used as a negative control.
