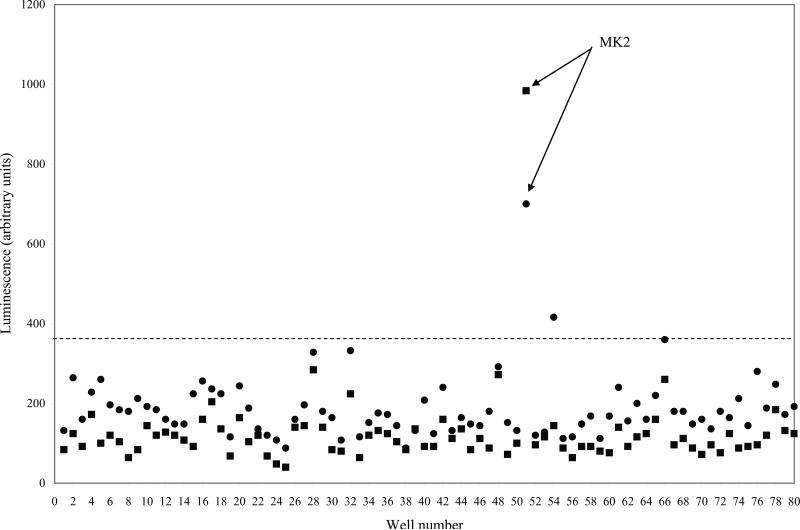
Fig. 1.
Knock-down of MK2 protects against Shiga toxicity. A siRNA screen of 646 human kinase and kinase-associated genes was adapted to a 96-well format (see Experimental procedures). Shown are two representative plates, run in duplicate (circles and squares), demonstrating light levels of 80 different kinase siRNAs after a 24-h treatment with STx1 (1 ng/mL). Well number represents each well of HeLa-Fluc cells transfected with 50 nM siRNA targeting a specific kinase, and corresponding light levels are shown on the y-axis. Control wells have been excluded (see Supplementary Fig. 2). A hit was considered any knock-down that maintained luminescence at least 3 standard deviations above STx1-treated controls (dotted line). Knock-down of MK2 (siRNA sequence provided in Experimental Procedures) conferred the highest protection against Shiga toxicity. Mean and standard deviations for each set of duplicate plates were determined by GraphPad Prism. MK2, mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2.