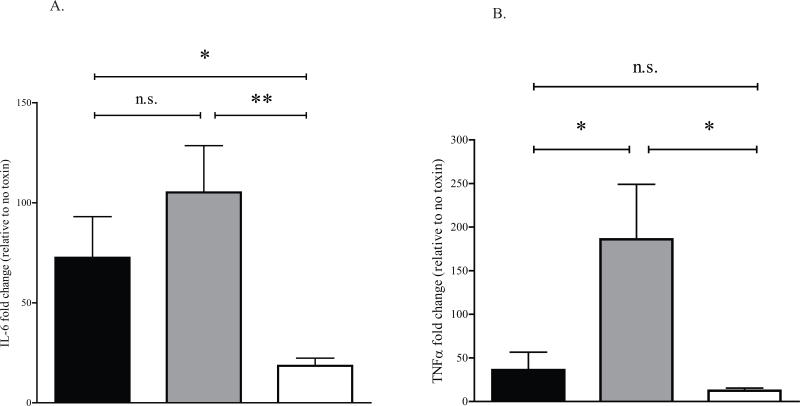
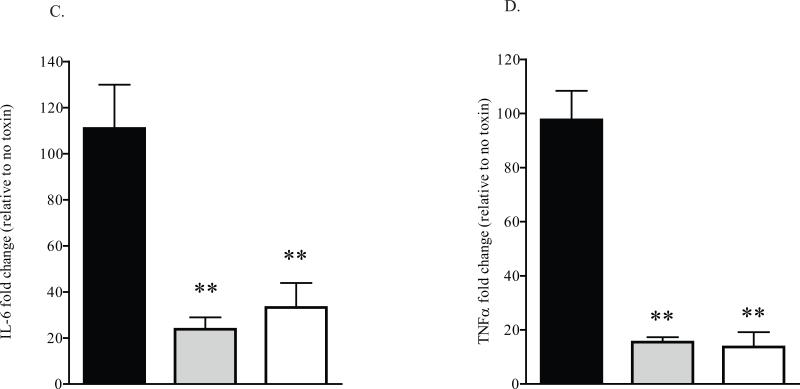
Fig. 6.
MK2 inhibition reduces the STx1-induced inflammatory response.
A. HeLa cells were transduced with a control adenoviral construct (pAd-Luc; black bars), a construct expressing wild-type MK2 (MK2-WT; gray bars), or a construct expressing a catalytically inactive MK2 (MK2-DN; white bars) for 24 h prior to treating with STx1 (10 ng/mL) for 6 h. The levels of IL-6 and TNFα mRNA were determined by qPCR and are expressed as a fold change above mRNA levels in transduced cells lacking STx1 (see Experimental Procedures). Data points represent duplicate data from three independent experiments (mean ±S.D.). Sample means were compared using a two-tailed Student's t-test for independent samples.
B. HeLa cells were pretreated with DMSO (0.5% v/v; black bars), the MK2 inhibitor PHA-781089 (20 μM; gray bars), or the p38 inhibitor SB202190 (10 μM; white bars) for 1 h prior to a 6-h exposure to STx1 (100 ng/mL). The levels of IL-6 and TNFα mRNA were determined by qPCR and are expressed as a fold change above mRNA levels in compound-treated cells in the absence of STx1. Data points represent duplicate data from three independent experiments (mean ±S.D.). Sample means were compared as in (A). n.s. denotes no significant change, * significant change (p<0.05), ** highly significant change (p<0.01).