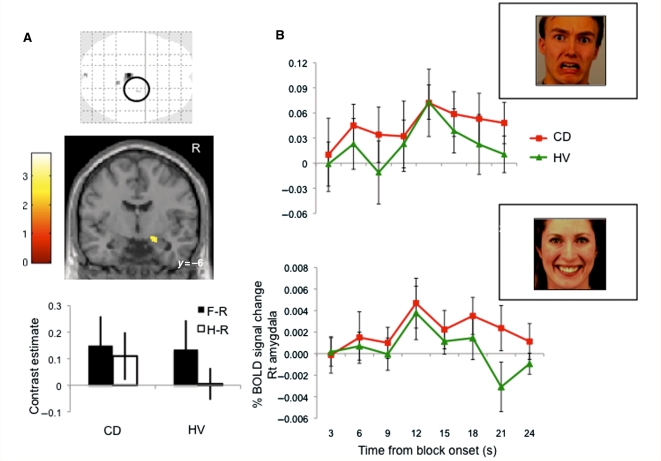
Figure 1.
Amygdala activity to emotional stimuli in conversion disorder (CD). (A) Patients with motor conversion disorder (CD) were compared with healthy volunteers (HV) using an incidental affective task with a mixed measures ANOVA with patient Group as a between-subjects factor and Valence as a within-subjects factor. The glass brain, statistical parametric map image and contrast estimates show the significant patient Group by Valence interaction of fearful versus rest (F–R) and happy versus rest (H–R) contrasts between patients with conversion disorder and healthy volunteers localized to the right amygdala (mixed measures ANOVA) (right amygdala local peak Montreal Neurological Institute coordinates x, y, z = 24, −4, −24 mm, Z = 3.83, P < 0.001 uncorrected, P < 0.05 region of interest corrected). The glass brain is shown at P < 0.001 uncorrected cluster threshold >4. The statistical parametric map image is shown at P < 0.005 uncorrected cluster threshold > 4. (B) Right amygdala time course activity. The area under the curve for the right amygdala time course (Finite Impulse Response function time-locked to block onset) was compared between patients with conversion disorder and healthy volunteers for the fearful (top; t = 1.81, P = 0.08) and happy (bottom; t = 2.96, P = 0.006) conditions. Error bars represent standard deviation.