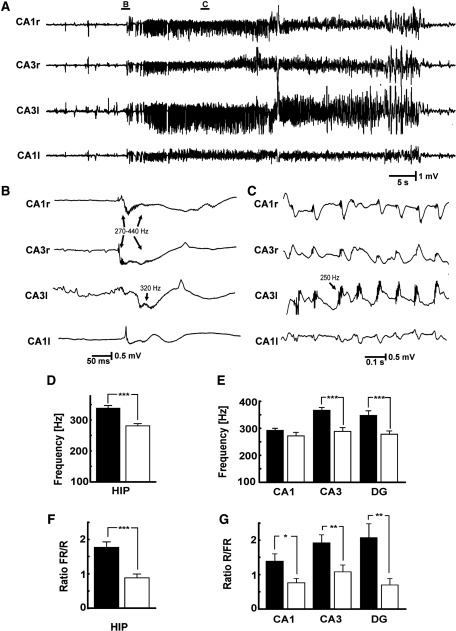
Figure 6.
Ictal HFA. (A) Typical seizure activity observed in tetanus toxin model of epilepsy: example of a seizure with ‘hypersynchronous’ onset. (B) Seizure onset occurs suddenly and is characterized by bilateral synchronous slow discharges that were first recorded in ipsilateral CA3 and propagated to ipsilateral CA1 and to the contralateral hippocampus. The HFA superimposed on this discharge was initially 440 Hz and later decreased to 270 Hz. HFA was also present in contralateral CA1. (C) HFA observed during ictal discharges. (D) Comparison of first spectral moment of ictal onset HFA between ipsi- and contralateral hippocampus. (E) Regional values of the first spectral moments. (F) Fast ripple (FR)/ripple (R) power ratio at ictal onset in the two hippocampi. (G) Regional differences of the ratios of fast ripples/ripples. Significance values are *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Only raw data are shown.