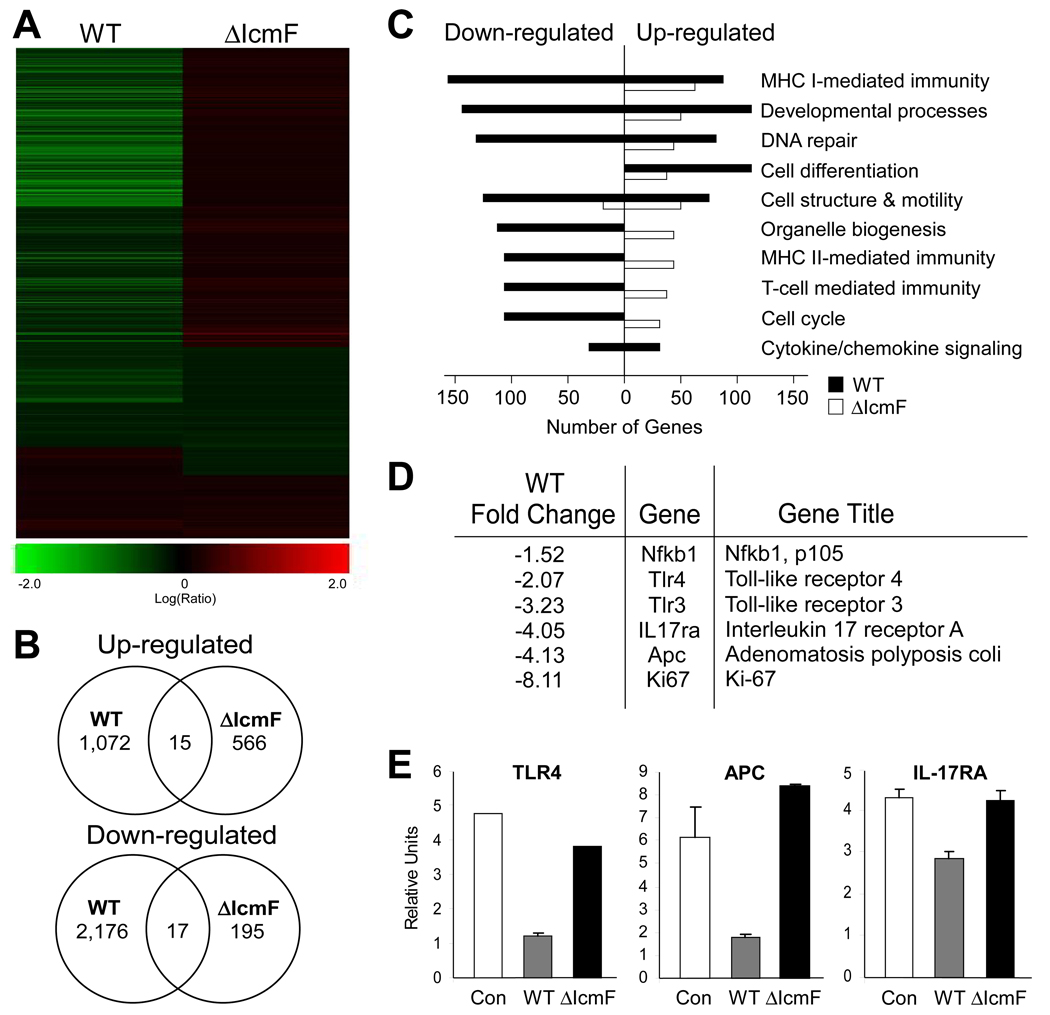
Figure 4. Wild-type H. hepaticus Induces a Wide Repertoire of Responses in MODE-K cells.
RNA was harvested from MODE-K cells incubated for 6hr with either wild-type H. hepaticus, ΔIcmF mutant, or no bacteria and analyzed by an Agilent Whole Mouse Genome Microarray. Gene expression of MODE-K cells incubated with bacteria was compared to transcript levels from RNA of untreated MODE-K cells. Only genes with a p-value <0.5 and fold change >1.5 were used for subsequent analysis.
(A) Heat-map analysis of MODE-K gene expression in the presence of WT or ΔIcmF shows massive down-regulation by wild-type H. hepaticus.
(B) Venn diagram showing up- and down- regulation of gene expression in the presence of WT or ΔIcmF.
(C) Gene ontogeny analysis of changes in MODE-K transcript levels for various functional groups. Wild-type bacteria down-regulate numerous cellular pathways.
(D) Fold change of select innate and adaptive immune genes in the presence of WT H. hepaticus.
(E) qRT-PCR analysis of RNA from MODE-K cells for genes associated withinflammation and colon cancer. Error bars show SEM.