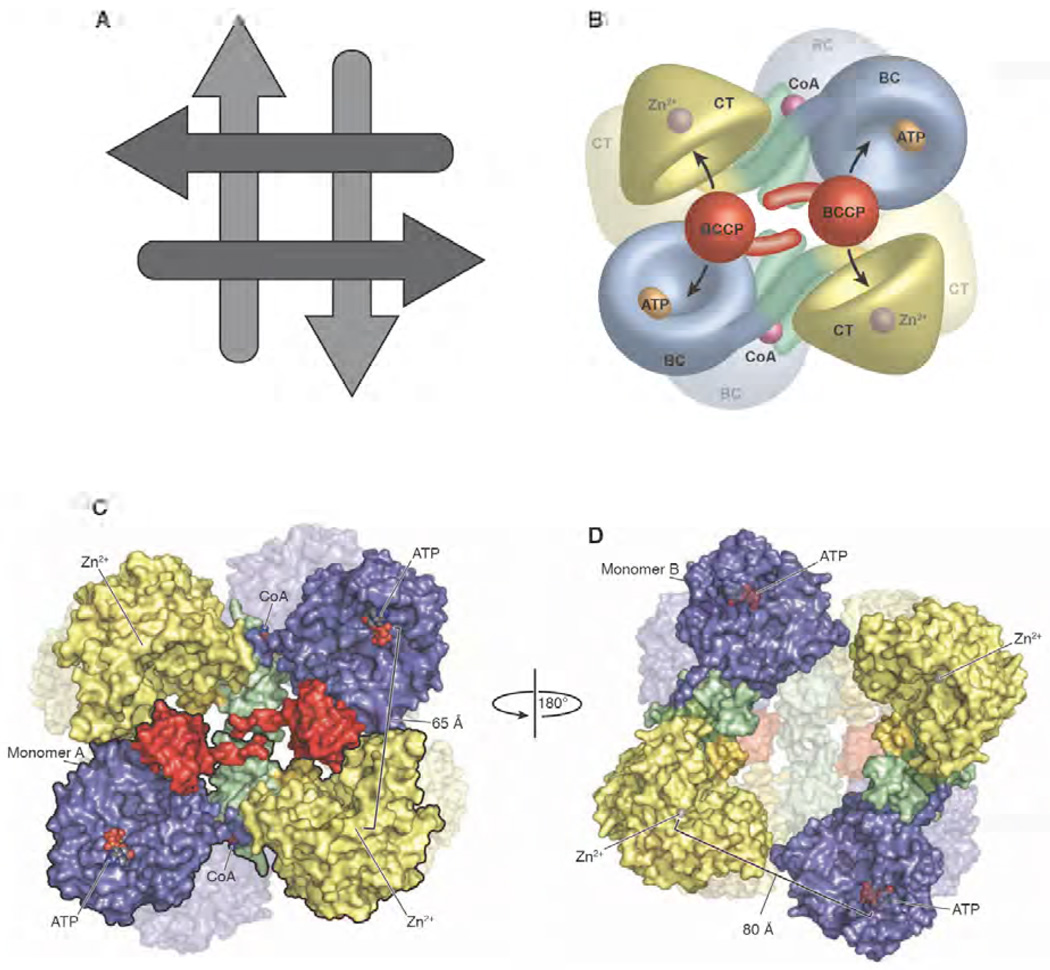
Figure 6. The quaternary structure of R. etli PC.
(A) Schematic representation of the arrangement of the individual monomers making up the tetramers. The arrows represent the general N-terminal to C-terminal direction of the individual polypeptide chains. The arrangement of the tetramer yields two distinct faces, with the monomers running antiparallel on each face and perpendicularly between the faces. (B) Model of the PC tetramer showing the movement of the BCCP domain between neighbouring active sites on opposing polypeptide chains [103]. (C) Surface representation of the top face of the tetramer with one of the two monomers outlined in black for clarity. The location of the ligand binding sites and the distances between them are indicated [103]. (D) Surface representation of the bottom face of the tetramer after a 180° rotation about the y axis. The distance between opposing active sites increases to 80 Å as a result of the altered orientation of the BC domain. The BCCP domain is disordered on the bottom face of the PC tetramer from R. etli and, consequently, is not modelled into the structure [103]. A,B and C are reproduced from [103].