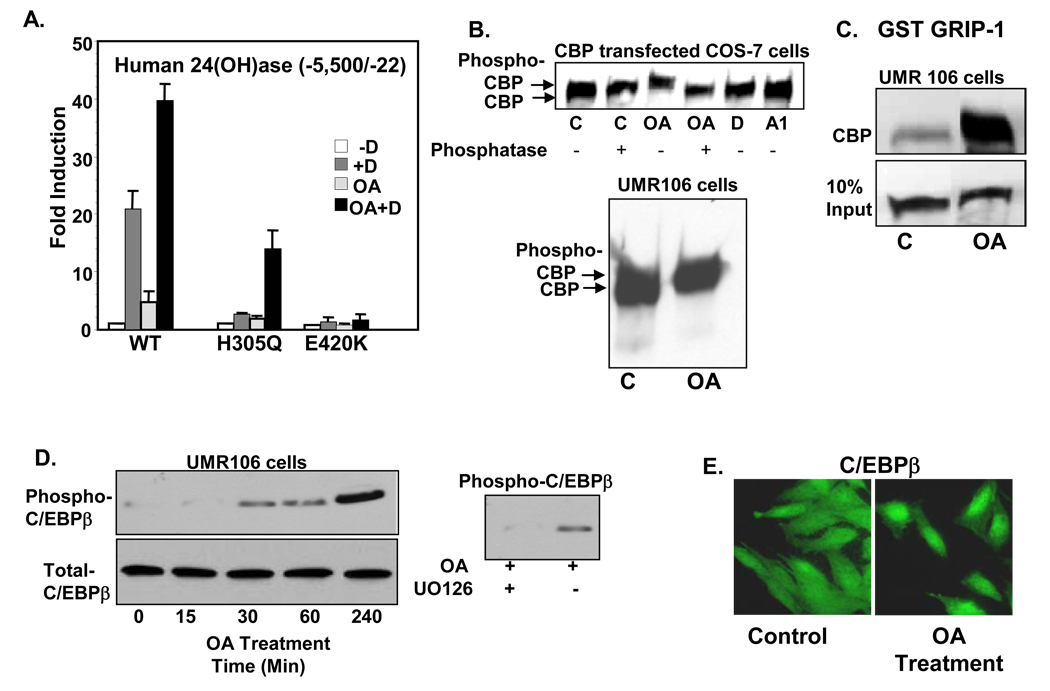
Fig. 2.
Partial activation of mutant VDR (H305Q) by phosphorylation and phosphorylation of coactivators mediated by okadaic acid (OA). A. COS-7 cells were transfected with the h24(OH)ase promoter and WT VDR or mutant VDRs (H305Q, E420K). Cell were treated with vehicle (−D), 10−8M 1,25(OH)2D3 (+D), 50 nM OA or 1,25(OH)2D3 + OA (OA + D). Note partial rescue of transcription of H305Q by phosphorylation. The E420K mutant (mutation in the coactivator binding site) was unresponsive to 1,25(OH)2D3 in the presence or absence of OA. B. Phosphorylation of CBP by OA treatment in COS-7 cells transfected with CBP were treated with vehicle (C), OA (50 nM), 1,25(OH)2D3 (D) or 1,25(OH)2D3 analog RO-262198 (A1) for 4h. UMR 106 cells were also treated with OA for 4h. C. GST pull down assay. Note enhanced interaction between GRIP-1 and CBP after OA treatment. D. Phosphorylation of C/EBPβ by OA and inhibition of C/EBPβ phophorylation by the MEK inhibitor UO126 (10 µM). E. Immunocytochemistry using C/EBPβ antiserum and fluorescence microscopy indicate that OA promotes nuclear accumulation of C/EBPβ in UMR 106 osteoblastic cells 2h after treatment.