Figure 10.
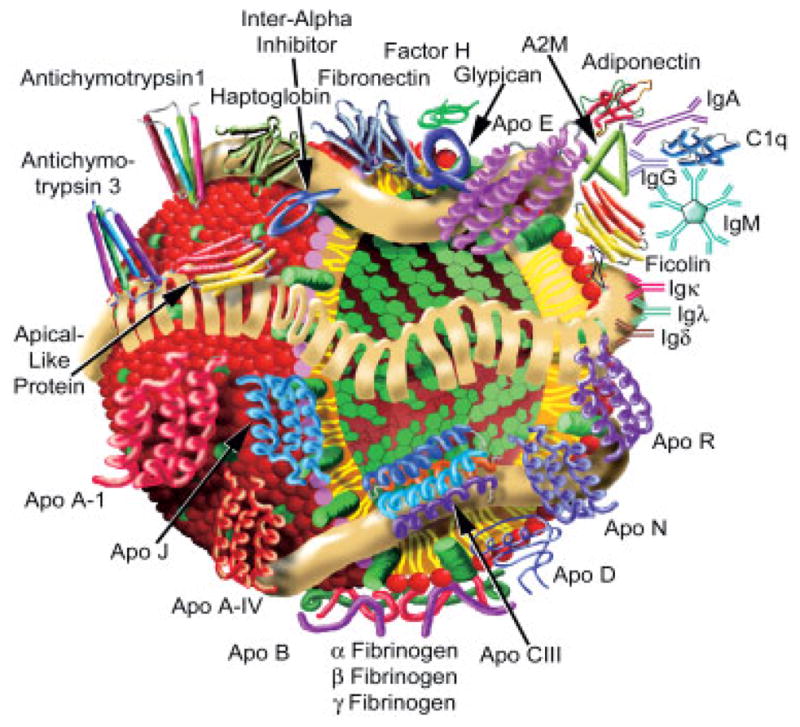
A hypothetical new model of LDL. Our current model of LDL isolated by gel filtration chromatography is a lipoprotein particle with a more complex and extensive proteome than previous models based on LDL isolated using high salt and high centrifugal force. Apolipoprotein B, with its amphipathic domains, forms a tight belt-like structure around the phospholipid surface and predominantly cholesteryl ester core. A constellation of other plasma proteins (Table 3) may interact with LDL transiently or for longer periods. Several of the interactions shown between peripheral proteins have been noted previously in other studies. This model of LDL serves to stimulate new experiments concerning the atherogenicity of LDL. Surface phospholipids: red spheres with yellow tails; surface free cholesterol: green barrels; core cholesteryl ester: green multi-rings.
