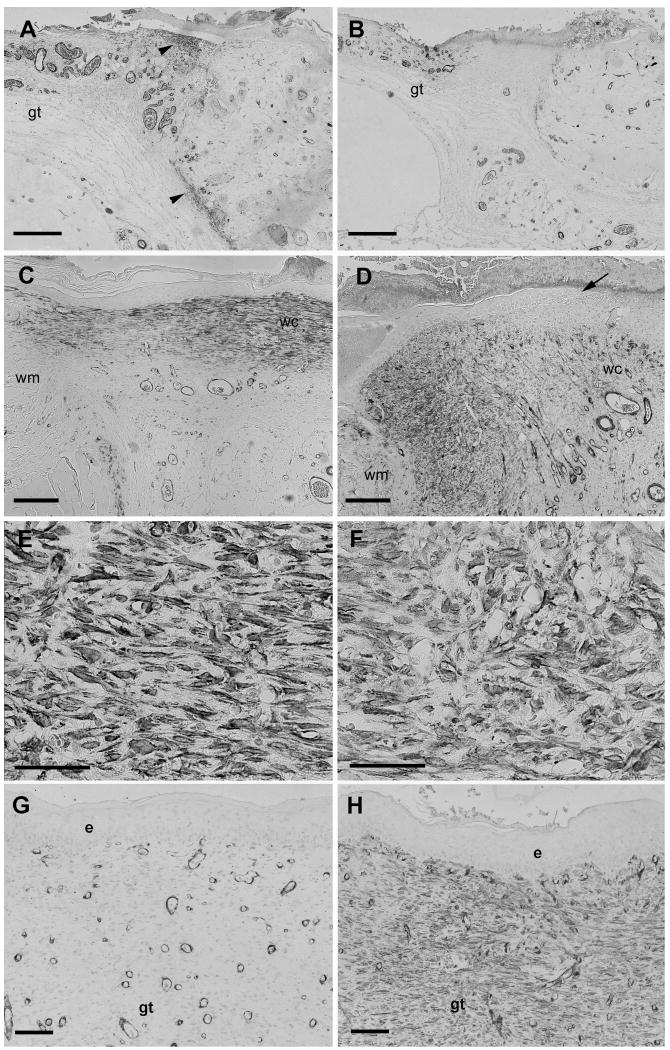
Figure 2.
SMAA immunostaining of wounds. Immunostaining for SMAA on postoperative days 4 (A, B), 8 (C-F) or 14 (G, H) showing tissue sections of full-thickness skin wounds untreated (A, C, E, G) or treated with the MMPI BB-94 (B, D, F, H). (A) SMAA-stained myofibroblasts are present in the superficial and deep dermis (arrowheads) close to the edge of control wound on day 4. Myofibroblasts are absent from the adjacent granulation tissue (gt). (B) Few SMAA-stained myofibroblasts are present in the BB-94-treated wound on day 4. (C) Strongly SMAA-stained myofibroblasts are present in granulation tissue that has been re-epithelialized from wound margin (wm) to wound center (wc) of control wound on day 8. (D) SMAA stained myofibroblasts are mainly located in granulation tissue near wound margin (wm) with few in wound center (wc). Newly formed epidermis terminates prior to wound center (arrow); SMAA-stained myofibroblasts are present primarily beneath new epidermis. (E, F) Higher magnification images of figures C and D. SMAA-stained myofibroblasts in granulation tissue in day 8 control wounds are aligned parallel to the wound surface (E); in contrast, SMAA-stained myofibroblasts in BB-94 treated wounds are more rounded and have an irregular organization (F). (G) Few SMAA positive myofibroblasts are present in wound center granulation tissue (gt) of control wound on day 14. Blood vessels with rounded lumina surrounded by darkly stained cells are oriented in parallel to the wound bed. (H) Numerous SMAA-stained myofibroblasts are present in wound center granulation tissue (gt) beneath epidermis (e) of BB-94 treated wound on day 14. Blood vessels are are predominantly oriented perpendicular to the wound bed. Scale bars: A-B, 600 μm; C-D, 500 μm, E-F, 20 μm, G-H, 100 μm.