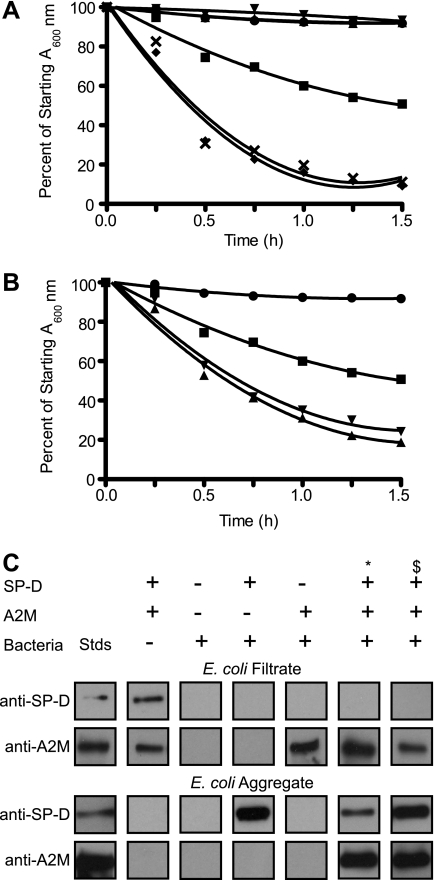
FIGURE 6.
A2M enhances the ability of SP-D to agglutinate E. coli, and SP-D, but not A2M, binds E. coli. A, SP-D, but not A2M, is able to agglutinate bacteria and cause a reduction in the A600 nm. A2M (50 or 5 μg/ml) or SP-D (1 μg/ml) was added to 200 μl of E. coli suspension in the presence of 5 mm CaCl2. The addition of A2M premixed with SP-D greatly enhances the agglutination of bacteria. A2M (50 or 5 μg/ml) and SP-D (1 μg/ml) were pre-mixed for 1 h at 37 °C in the presence of 5 mm CaCl2 prior to being added to 200 μl of bacterial suspension. ●, bacteria alone; ■, bacteria + 1 μg/ml SP-D; ▴, bacteria + 50 μg/ml A2M; ▾, bacteria + 5 μg/ml A2M; ♦, bacteria + 50 μg/ml A2M and 1 μg/ml SP-D premixed; ×, bacteria and 5 μg/ml A2M + 1 μg/ml SP-D premixed. The bacteria and bacteria + A2M alone conditions are overlapping with each other on the graph. All values are significantly different from the SP-D alone condition (p < 0.01). B, pre-mixing the bacteria with A2M enhances E. coli agglutination by SP-D, but not as much as pre-mixing the SP-D and A2M prior to addition to the bacterial suspension. A2M (50 or 5 μg/ml) was mixed with the bacteria suspension for 1 h at 37 °C prior to SP-D (1 μg/ml) addition in the presence of 5 mm CaCl2. ●, bacteria alone; ■, bacteria + 1 μg/ml SP-D; ▴, bacteria pre-mixed with 50 μg/ml A2M then 1 μg/ml SP-D; ▾, bacteria pre-mixed with 5 μg/ml A2M then 1 μg/ml SP-D. All values are significantly different from the SP-D alone condition (p < 0.01). All experiments were conducted at the same time but plotted separately for clarity (A and B). Results are representative of three independent experiments. Error bars indicate S.E. C, bacterial-SP-D·A2M immune complexes from the agglutination assays were separated from the filtrate. The presence of SP-D and A2M in these complexes was determined by Western blot analyses. A2M is present in the filtrate (top 2 panels) and is only present in the aggregate fraction when SP-D is present (bottom 2 panels), suggesting that A2M does not bind to the bacteria but does bind to the SP-D. Conditions: A2M, 50 μg/ml; SP-D, 1 μg/ml; *, A2M and SP-D premixed before being added to bacteria; $, A2M and bacteria premixed prior to SP-D addition.