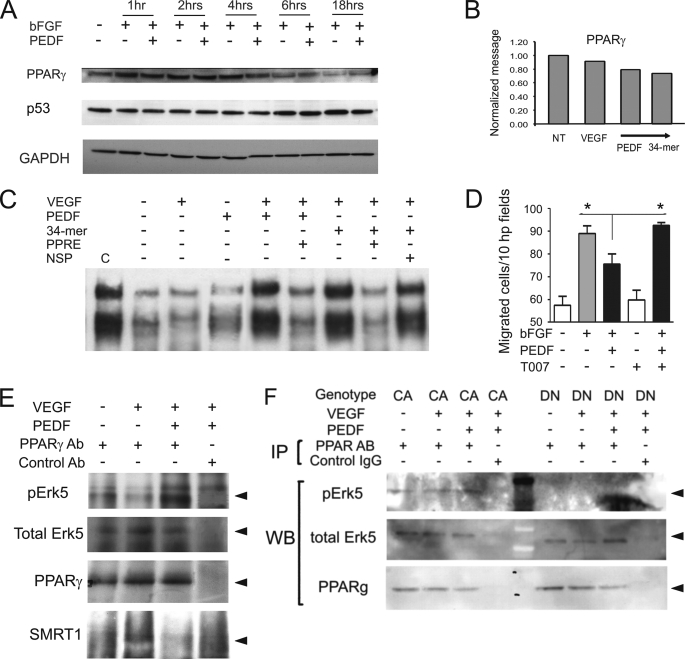
FIGURE 4.
Erk5 in the PPARγ transcription complexes is phosphorylated in response to PEDF. A, HMVECs were treated for the indicated time periods with the combinations of bFGF (10 ng/ml) and PEDF (10 nm). PPARγ and P53 levels were measured by Western blot. B, total RNA was extracted and PPARγ mRNA measured by real-time RT-PCR after 6 h of treatment. C, PPARγ mobility shift assay. HMVECs were treated with VEGF ± PEDF or the 34-mer, nuclear extracts were collected and subjected to EMSA with biotinylated PPRE probe. Non-biotinylated wild-type and non-biotinylated mutant PPRE probes were used as specific and nonspecific competitors (PPRE and NSP, respectively). C indicates positive control. D, PPARγ is necessary for PEDF inhibitory activity. HMVECs chemotaxis up the bFGF gradient (20 ng/ml across the membrane) was blocked by PEDF (20 nm) alone or in the presence of T0070907 (100 nm) Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences (p < 0.05, calculated by one-tailed Student's t test). E, wild-type HMVECs (MEK5-WT) were treated with PEDF, VEGF, or VEGF+PEDF. Untreated cells served as a negative control. Cell lysates were collected and subjected to immunoprecipitation with PPARγ antibody followed by Western blot with antibodies for p-Erk5, total Erk5, and SMRT. The input was controlled by Western blot with PPARγ antibody. F, HMVECs expressing MEK5-DN or MEK5-CA, were treated with VEGF (1 ng/ml) and PEDF (10 nm). Protein extracts were precipitated with PPARγ antibody and analyzed by Western blot for p-Erk5 and total Erk5. The input was controlled by Western blot with PPARγ antibody.