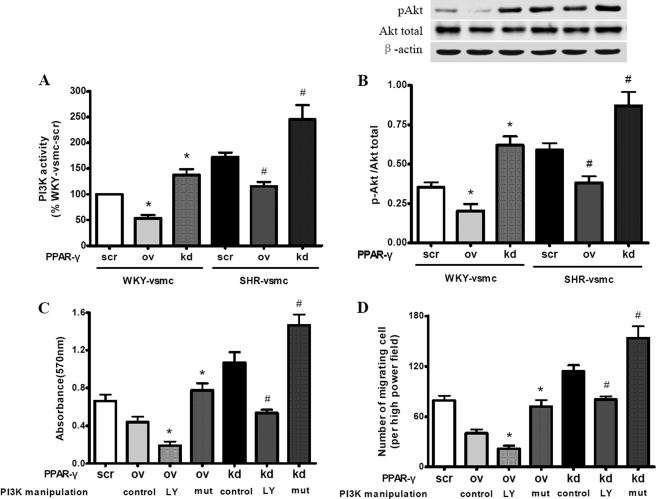
FIGURE 8.
Role of PI3K/Akt signaling in PPAR-γ-mediated regulation of proliferation and migration in VSMCs. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and Western blot were used to determine the PI3K activity and p-Akt level, respectively. MTT assay and a modified Boyden chamber were used to determine the proliferation and migration of VSMCs. A and B, effect of PPAR-γ on PI3K activity (A) and p-Akt level (B). Compared with WKY-VSMC, SHR-VSMC showed markedly enhanced PI3K activity and p-Akt levels. PPAR-γ overexpression reduced PI3K activity and p-Akt levels in SHR-VSMC, whereas PPAR-γ silencing had the opposite effects in these cells. The same effect of manipulated PPAR-γ was also observed in WKY-VSMC. C and D, effect of PI3K on PPAR-γ-mediated regulation of proliferation (C) and migration (D) in SHR-derived VSMCs. LY294002 impeded the elevated proliferation and migration induced by PPAR-γ silencing, whereas active PI3K mutant had the opposite effect. In contrast, reduced proliferation and migration by PPAR-γ overexpression were reversed by active PI3K mutant, and further inhibited by LY294002. Data are presented as mean ± S.E. (n = 5). For A and B, *, p < 0.05 versus WKY-VSMC with PPAR-γ-scr; #, p < 0.05 versus SHR-VSMC with PPAR-γ-scr. For C and D, *, p < 0.05 versus PPAR-γ-ov control; #, p < 0.05 versus PPAR-γ-kd control. LY, LY294002; mut, constitutively active PI3K mutant.